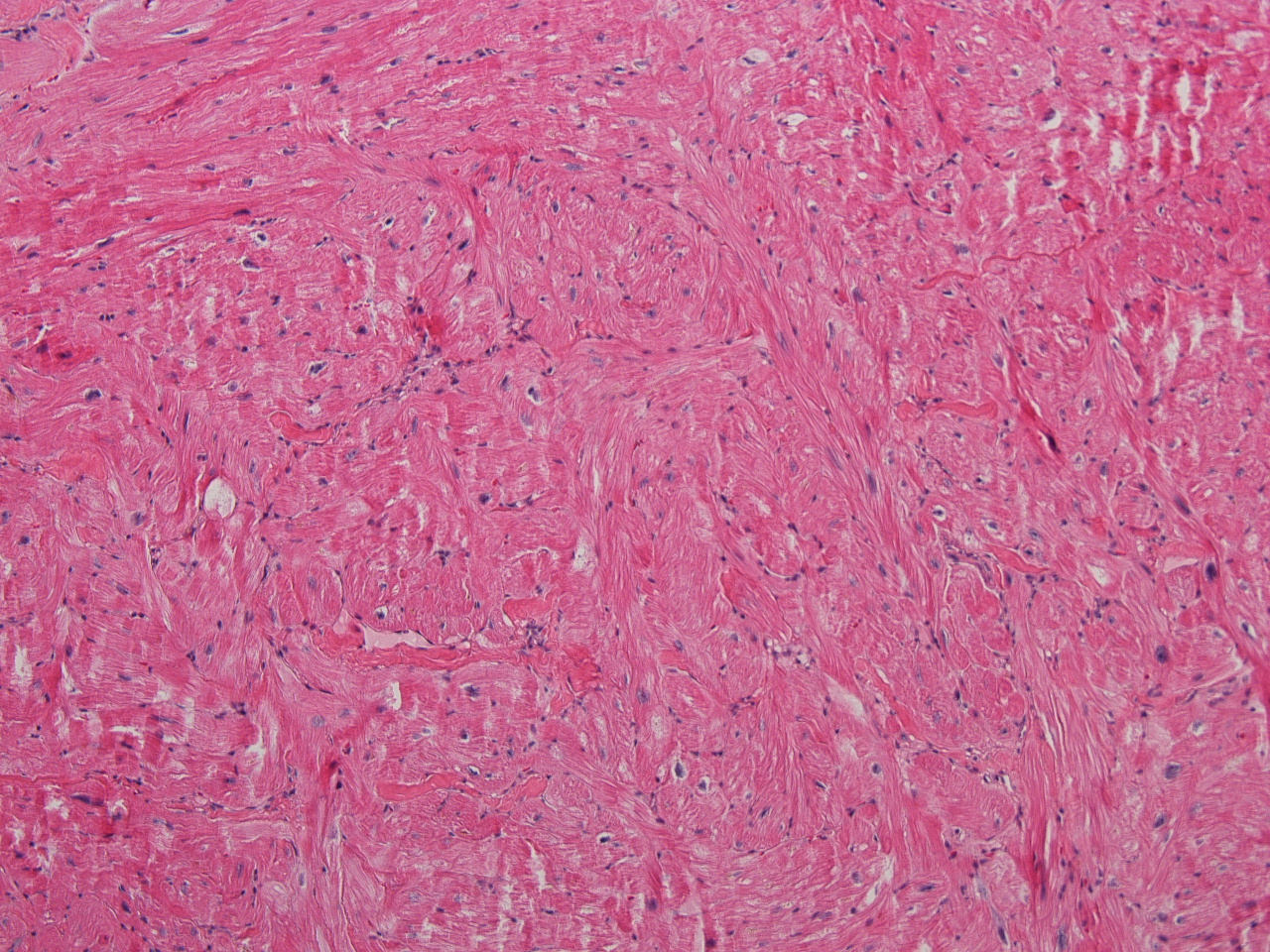
37 yo postpartum F w/ ADHF. Imaging: RVH. H/o long QT. Sudden death of a sibling. Lft ventricle bx.
Which of the following diagnoses best describes this lesion?
A. Amyloidosis
B. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
C. Hemochromatosis
D. Peri-partum cardiomyopathy
Answer
The answer is “B”,Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (Example “A”, Granular cell tumor).
The clinicians’ differential diagnosis was hypertrophic cardiomyopathy vs infiltrative cardiomyopathy. The image clearly show marked myofiber disarray characteristic of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Fibrosis is frequently seen in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy but is unremarkable in this case. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common cardiac inherited disorder caused by mutations in a variety of sarcomeric genes and is the most common monogenic inherited cardiac disease. Genetic testing for the disorder is commercially available. Histology can be characteristic however endomyocardial biopsy may be unremarkable because the changes are only present in deep myocardium. The disorder is generally diagnosed by clinical and imaging modalities followed by genetic testing.
Amyloidosis and hemochromatosis are infiltrative cardiomyopathies. In amyloid heart, interstitial widening with eosinophilic materials is identified and confirmed by Congo Red stain. Hemochromatosis can usually be visualized as intramyocyte pigment that is confirmed to be iron by staining.
Post-partum heart failure is a recognized syndrome of heart failure in the peri-partum period. The pathogenesis is somewhat cryptic pathogenesis The diagnosis of peri-partum cardiomyopathy requires the absence of preexisting cardiac disease and has no recognizable morphologic correlates.
References
- Cardiovascular Pathology 4
th
- ed
- Jagdish Butany and Maximilian L. Buja
- Bejar D, Colombo PC, Latif F, Yuzefpolskaya M. Infiltrative Cardiomyopathies.
- Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2015 Jul 8;9(Suppl 2):29-38.
Contributed by Tom Winokur, MD