Case History
The patient is a 29 year-old female with clinical history of shortness of breath and fevers. Routine imaging studies showed multiple pleural nodules. CBC and routine chemistries are within normal limits with mild increase of LDH. Open biopsy of the nodules obtained.
What is the diagnosis?
- Mesothelioma
- Germ cell tumor
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma
- Thymoma
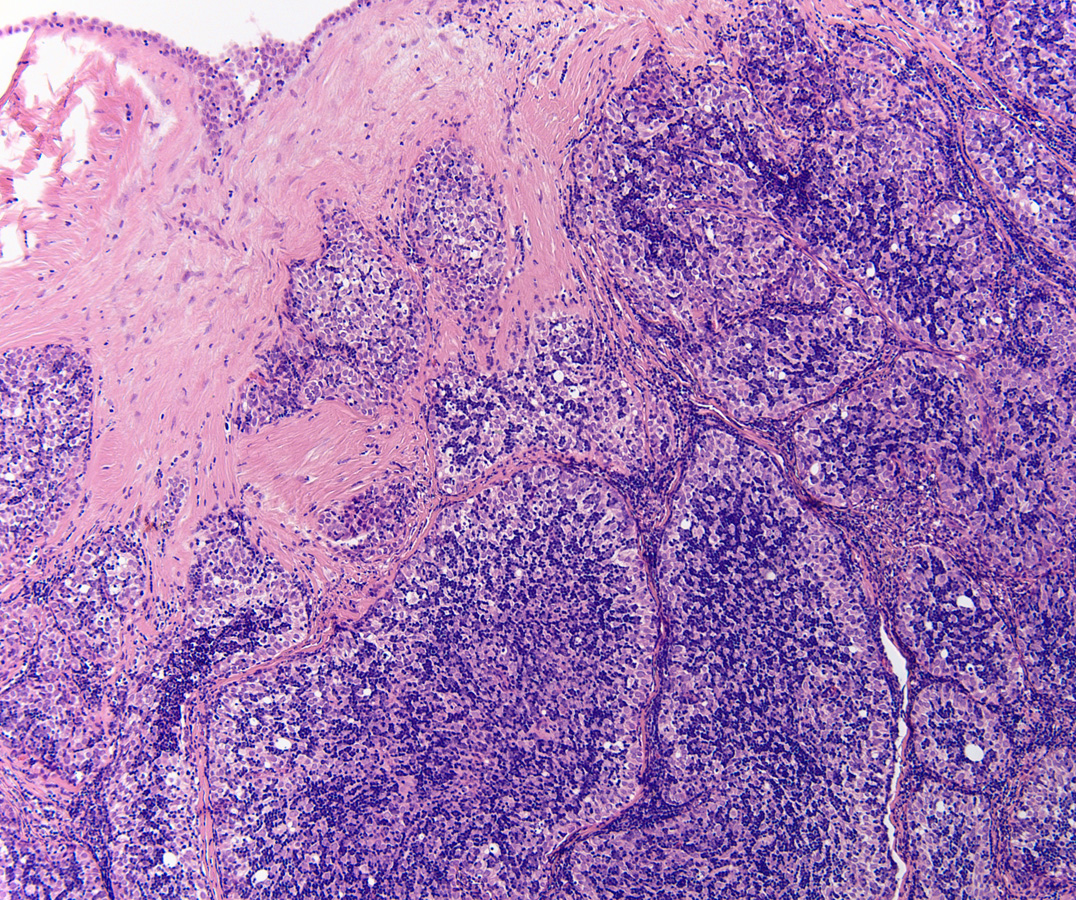
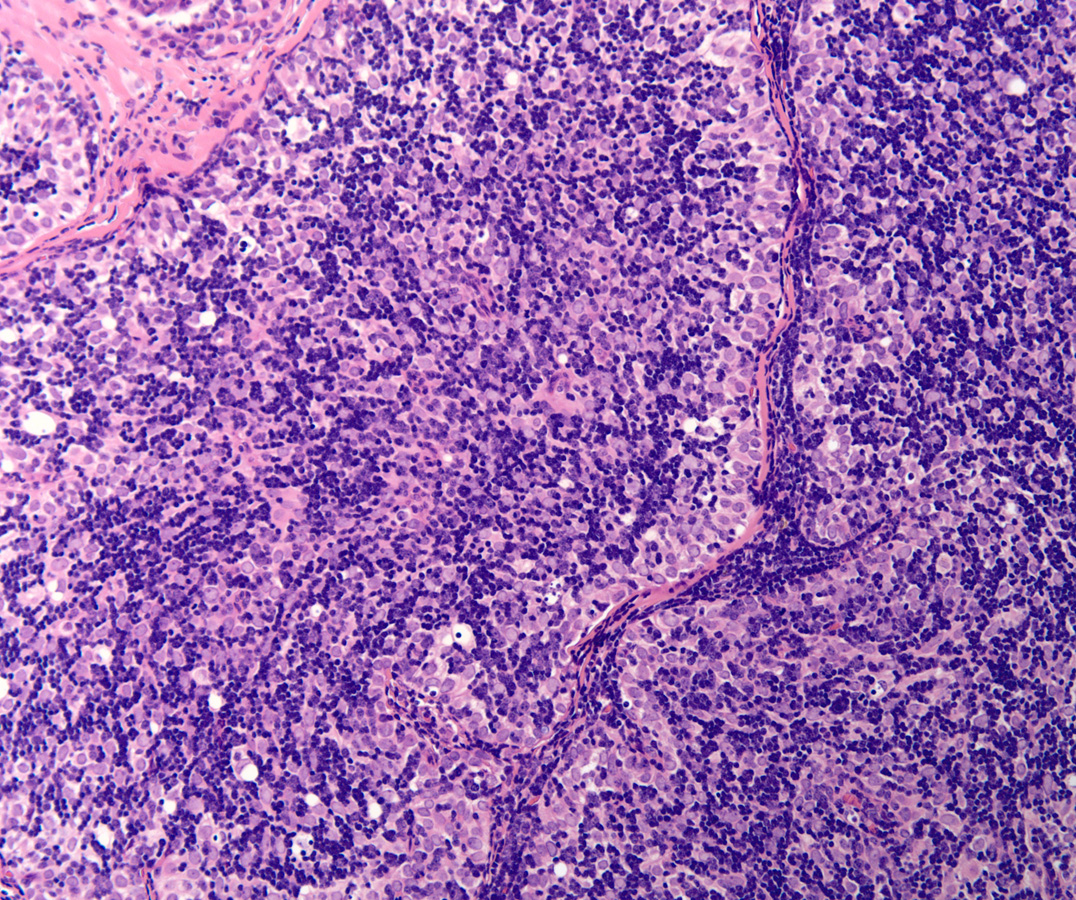
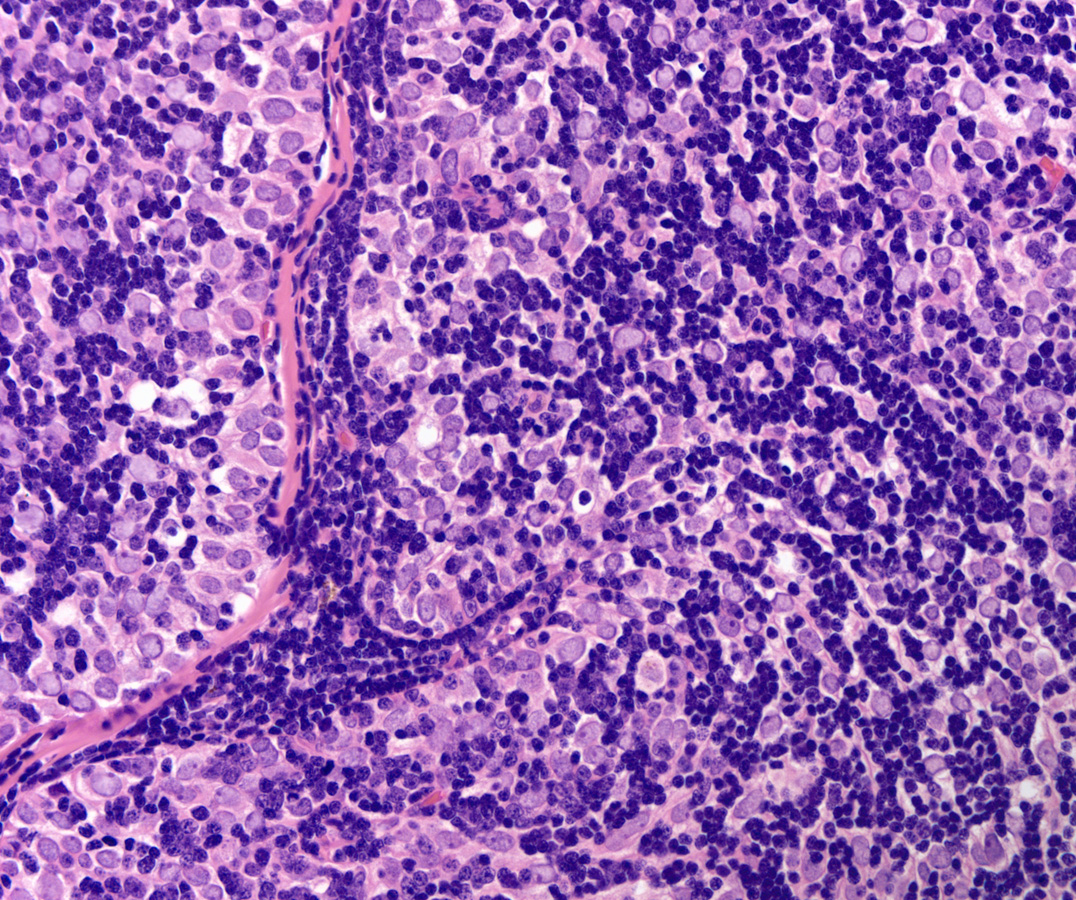

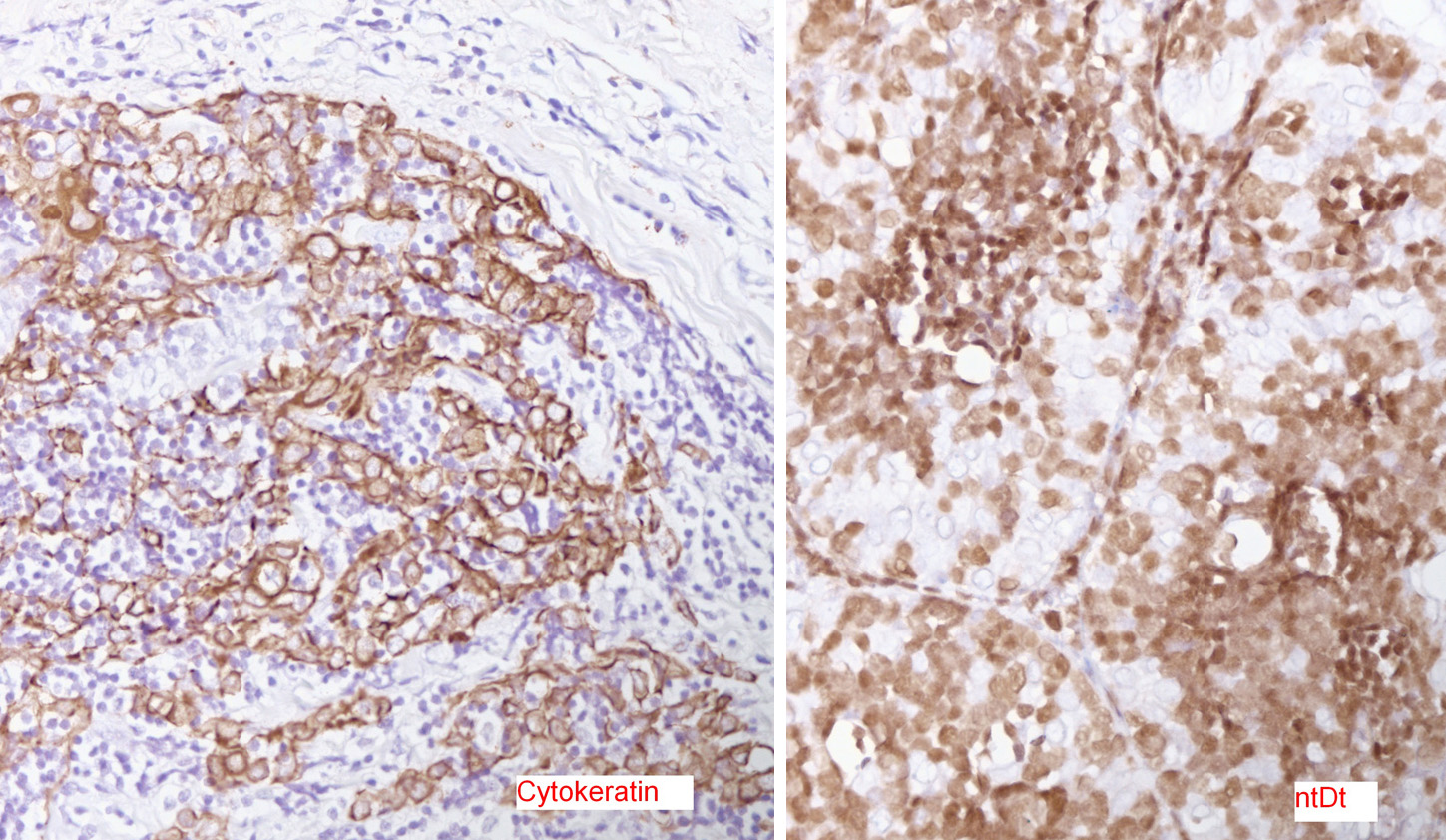
The answer is “D. Thymoma, WHO B2”
Discussion:
Low power H&E show tumor in below the mesothelial lining. Distinct lobular / organoid appearance noted with two types of cells, small lymphoid cells and large neoplastic cells with clear cytoplasm (bi-phasic pattern). IHC stains showed large cells are cytokeratin positive and small lymphoid cells expressed CD3, CD5 and ntDt (immature thymocytes).
Additional history later revealed a large anterior mediastinal mass with tracheal compression and seeding of pleura. Main tumor was not resectable. Histology (epithelial elements and thymic lymphoid stroma) and IHC stains support an aggressive thymoma, WHO B2, metastatic to pleura. Normal thymic milieu i.e. immature thymocytes often present in metastasis along with neoplastic epithelial component. Metastatic thymoma must be considered in the differential diagnosis with bi -phasic patten as illustrated above.
Ref: Weissferdt A et al. Thymoma: A clinicopathological correlation of 1470 cases. Humn Pathol. 2018;73:7-15.
Case contributed by Vishnu Reddy, M.D., Professor, Laboratory Medicine and Division Director, Neuropathology, UAB Department of Pathology