Case History
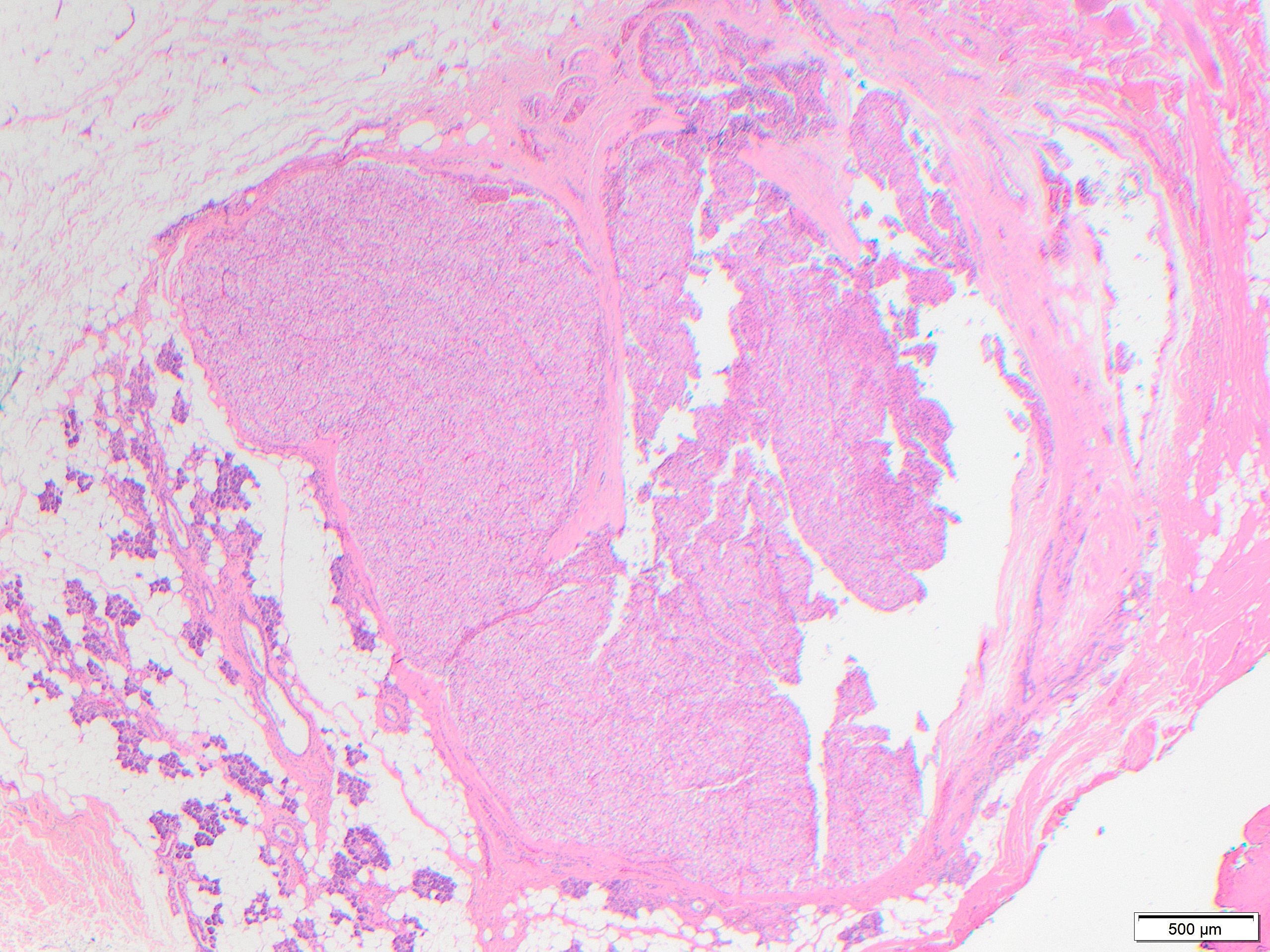
An elderly man presented with recurrent parotitis, a 1.8 cm enhancing nodule and innumerable enhancing <1 cm nodules in bilateral parotids. PAX-8 negative.
The most likely diagnosis is:
A. Oncocytic carcinoma
B. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma
C. Multifocal nodular oncocytic hyperplasia
D. Salivary duct carcinoma
Answer: B. Multifocal Nodular Oncocytic Hyperplasia (MNOH) with clear cell change
Discussion:
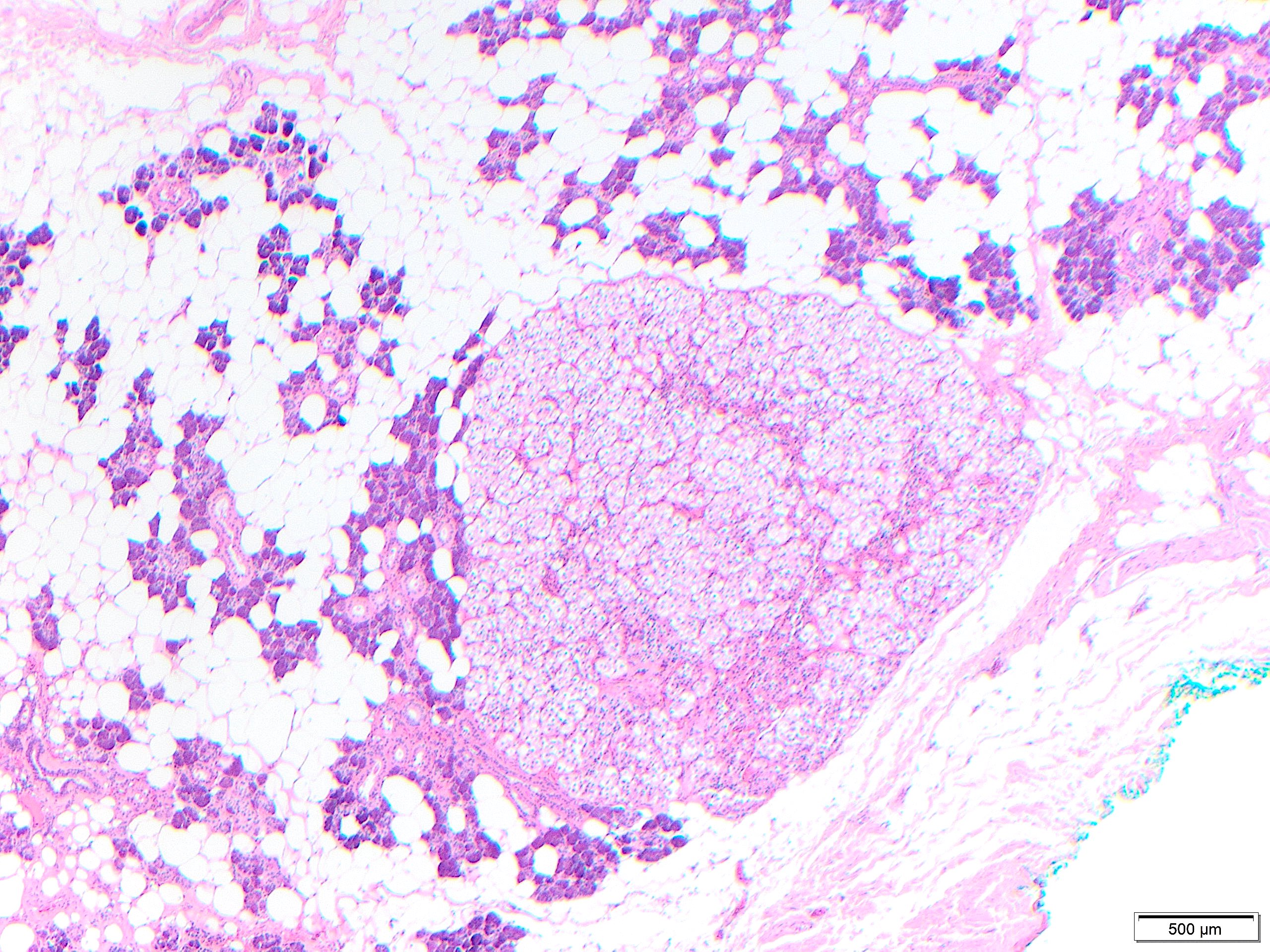
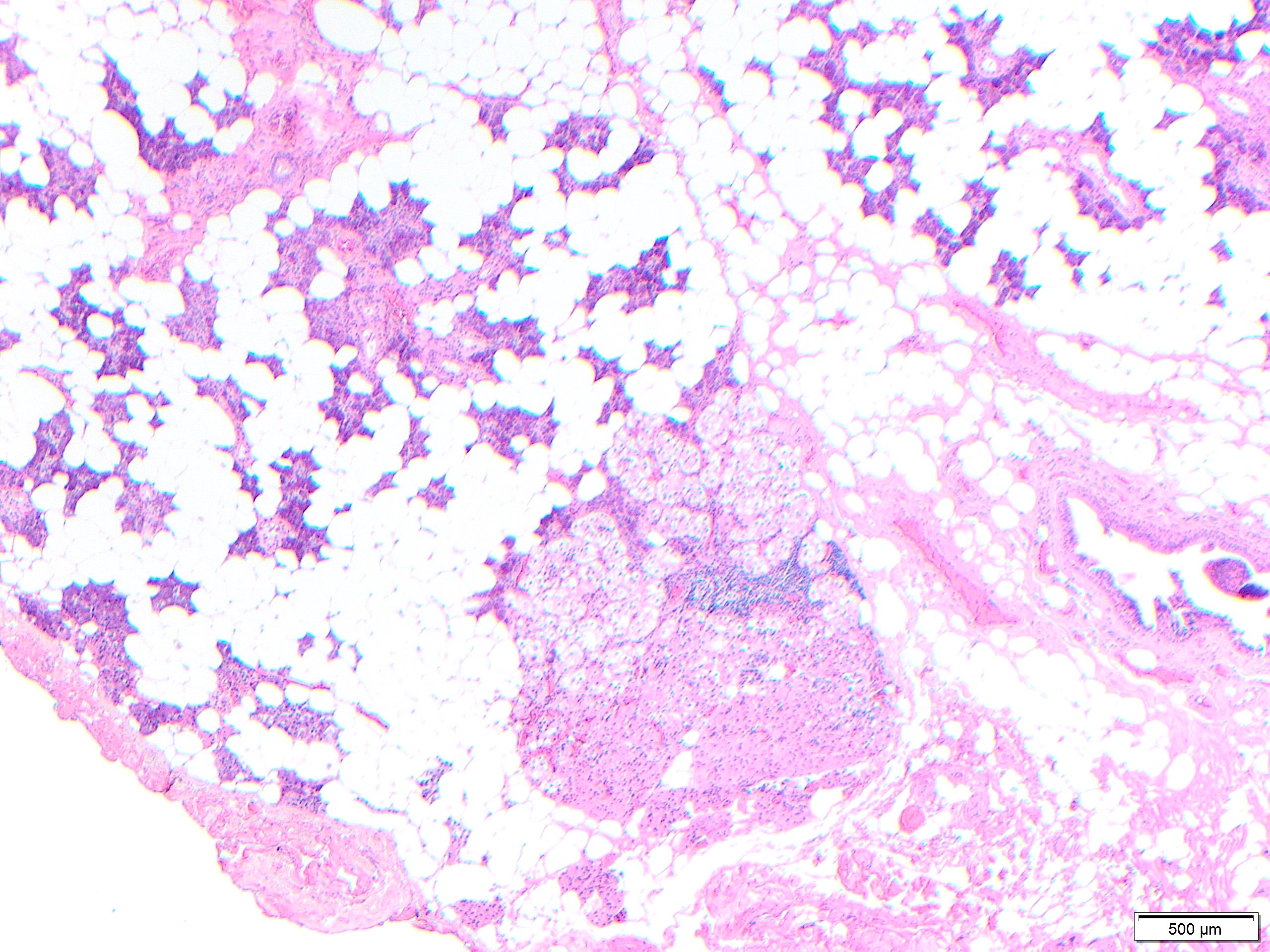
MNOH is a benign proliferation composed of multiple discrete nodules of oncocytes without a capsule. Oncocytic changes are more common in the major salivary glands, especially the parotid gland. Most cases are asymptomatic and occur in older patients, in their 70s to 90s.
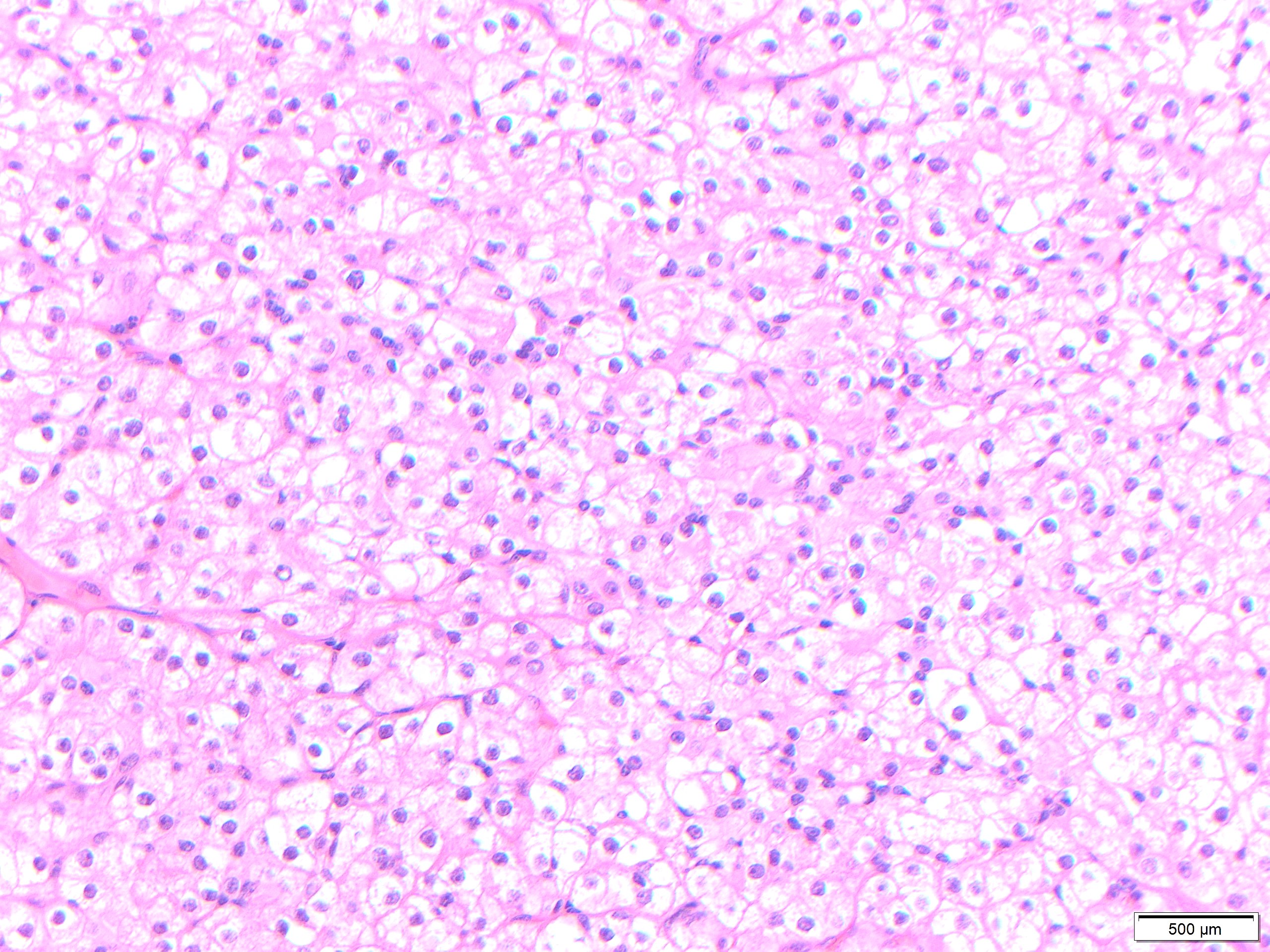
Oncocytes are large polyhedral epithelial cell, with low nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm. An oncocytoma is a benign mass forming neoplasm that is composed exclusively or predominantly of oncocytes, generally distinct from isolated collections or nodules of oncocytes and with a thin capsule. Oncocytosis is a diffuse oncocytic metaplastic process in the salivary gland with normal lobular architecture.
While eosinophilic cytoplasm in oncocytes results from excess mitochondria, they can undergo clear cell change as a result of glycogen accumulation in turn resulting in cell border accentuation due to margination of mitochondria. This change frequent in multinodular oncocytic hyperplasia.
Occasionally a dominant larger nodule occurs in the context of MNOH, and neoplastic versus hyperplastic origination is still debatable but of little clinical relevance. Larger nodules may have irregular fibrosis around them, as seen in oncocytic hyperplasias in other organs. When nodules of oncocytes are identified in the parenchyma immediately adjacent to an oncocytoma, these should not be interpreted as invasion or multiple oncocytomas, but should be interpreted as part of multifocal nodular oncocytic hyperplasia.
The clear change may be so prominent that may mimic metastatic renal cell carcinoma. The background changes from the other photos and negative staining with PAX-8 help in this distinction. Salivary duct carcinoma may display oncocytic change but would also show nuclear pleomorphism, necrosis, and invasive growth.
Reference
Tumors of the Salivary Glands. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology atlases of tumor and non-tumor pathology, Fifth Series. Bishop, Thompson, Wakely, Weinreb. 2021. ARP Press.