Research & Innovation
Historically, Americans have chosen conflict avoidance over violence in property rights.
Research shows that young children are at a particular risk for pedestrian injuries in parking lots, and interventions should be made to decrease this risk.
Airway fractal dimension gives added prognostic information over traditional CT scan measures in COPD.
Sensory processing difficulties, which affect one in six people, can make public spaces a nightmare and lead to traumatic meltdowns. A UAB expert teaches venues around the world how to help rather than hurt. Here’s her advice.
The International Symbol of Access has been criticized for its inadequate representation of disability diversity, poorly representing universal design of space and products.
A new discipline sits at the intersection of neuroscience and engineering, where lessons learned from circuits, networks and chips are combined with the latest findings on brain circuitry.
UAB professors publish distinct conceptual framework for entrepreneurship in educational settings.
A new screening tool developed at UAB has been shown to be an effective aid in determining the severity of cognitive issues.
Groundbreaking research from UAB shows that out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is the third leading cause of years lost and years lived with a disability due to a disease.
Attention, reasoning and memory could be improved with resistance exercise, according to a UAB study.
Researchers found that regular tenofovir gel users were associated with reduced risk of HSV-2 infection.
UAB researchers found spending 20 minutes in an urban park will make someone happier — whether they are engaging in exercise or not during the visit.
Safe and effective therapeutic agents that can treat these cancer-causing viruses are greatly needed.
All academic areas saw increases in grant award monies from November 2017 through October 2018 as the university continues to grow its mission.
The study’s findings show the benefits of the ketogenic diet in cancer patients, and the authors hope to expand their research to see if it will also impact cancer treatment.
The National Cancer Institute highlighted research from UAB that shows how the epigenetic plant-based diet in mice can prevent cancer more effectively at younger ages.
A gene mutation causes wrinkled skin and hair loss; turning off that mutation restores the mouse to normal appearance.
Significant novel findings published by UAB researchers established verapamil as a successful therapeutic approach to target loss of beta cell function caused by Type 1 diabetes.
A diabetes drug suggests potential therapy for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, based on research with human lung fibroblasts and a mouse model of lung fibrosis.
UAB is one of six universities in the world currently investigating the medicinal benefits of psilocybin.
In a large-scale analysis, Jeremy Blackburn, Ph.D., and collaborators found that the misuse of web archive services cause loss of ad revenue for popular news websites.
mediKanren, an "analytic engine" designed by UAB researchers, can sift 97 million assertions in seconds to find new treatments for patients and research avenues for scientists.
Hair’s graying is linked to innate immune response, activation of which can decrease pigmentation in hair.
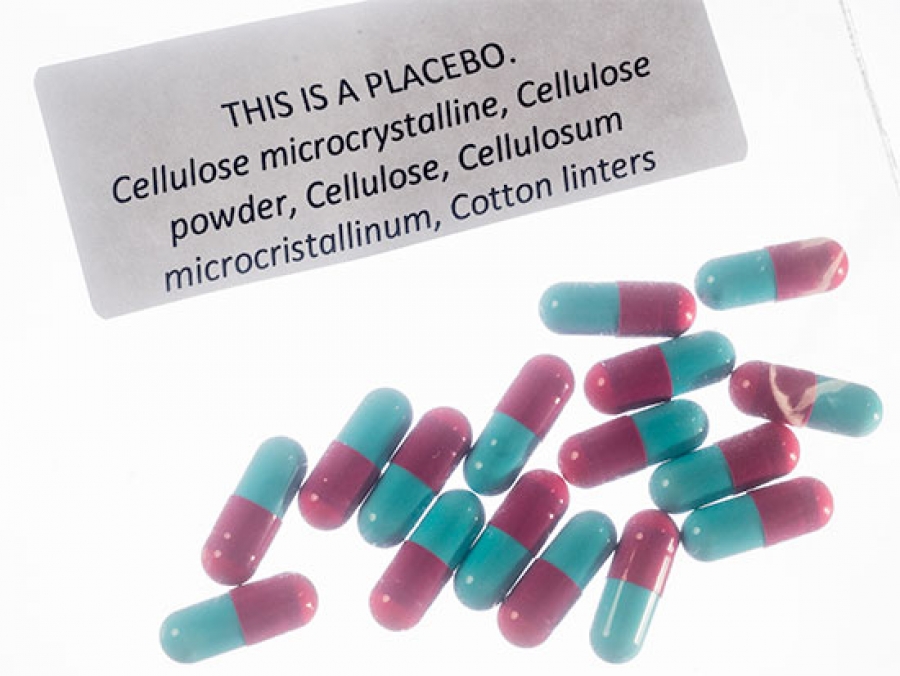
Fatigue in cancer survivors is significantly reduced by placebo pill, even when it is known it is a fake pill.
UAB ranked 15th nationally among public universities in research expenditures and topped $238 million in NIH funding for FY 2016.
Local retailers should find ways to get involved in the community to help boost business, according to a UAB study.
This more comprehensive approach may be needed to find ways to delay the progressive heart failure.
With an economic impact now exceeding $7.15 billion, according to Tripp Umbach, Alabama’s largest single employer’s influence on the state’s economy has grown by more than 50 percent since the last study.
Low dietary potassium leads to calcified arteries and aortic stiffness, while increased dietary potassium alleviates those undesirable effects in a mouse model, suggesting dietary potassium may protect against heart disease and death from heart disease in humans.
UAB research suggests EEG headsets, growing in popularity among consumers, need better security.