Research & Innovation
New findings from UAB researchers indicates that preventable environmental factors like repeated blows to the head in contact sports and pesticides and herbicides account for a substantial number of Parkinson’s disease cases.
While it has long been thought that the most direct health effect linked to the sanitation crisis in the Black Belt was due to soil-transmitted hookworm, a study led by UAB found no evidence of transmission.
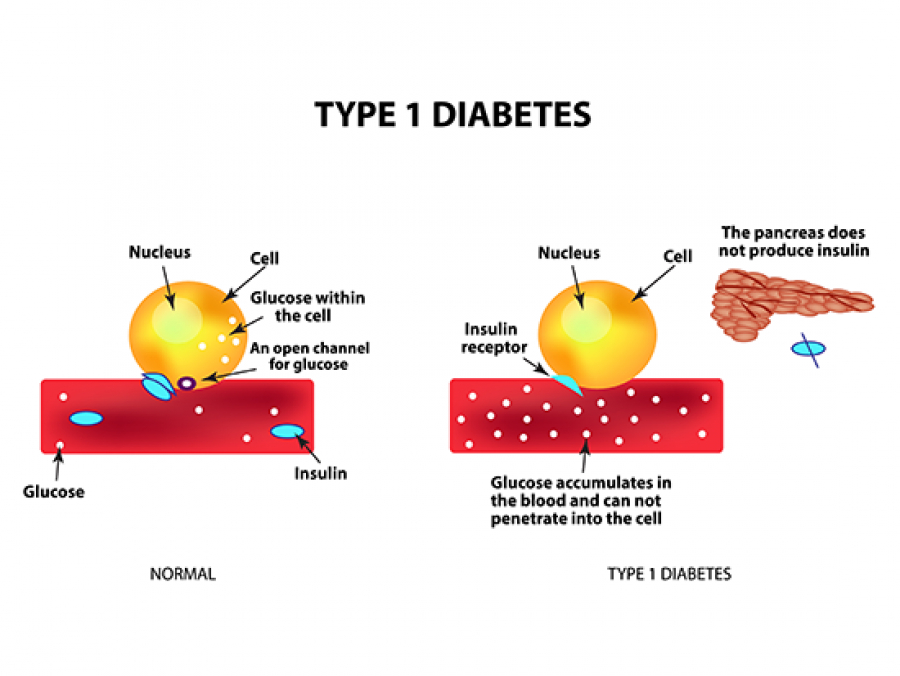
Vaccination of neonatal mice with group A Streptococcus promotes clonal expansion of B cells that produce antibody against GlcNAc. The association of reduced Type 1 diabetes risk after group A Streptococcus infection is dependent on these GlcNAc-specific B cells.
This is the largest grant the Department of Political Science and Public Administration has received.
The research team’s goal is to create a customizable solution that can be applied across various health care settings to reduce overcrowding in emergency departments.
Tuberculosis, the world’s leading infectious disease killer, caused 1.6 million deaths in 2021, along with 10 million new cases of tuberculosis every year.
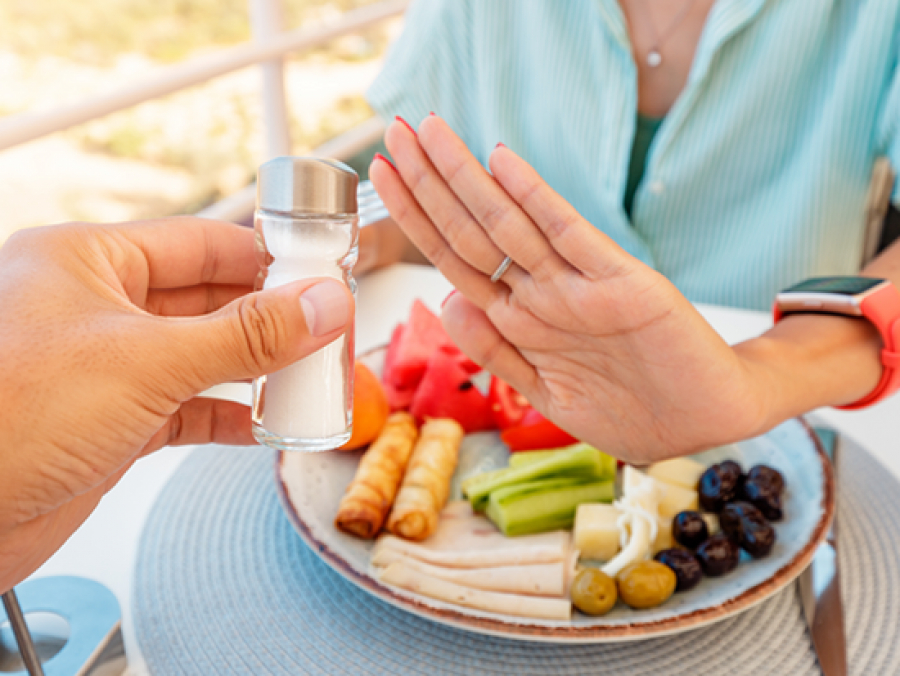
The study found that 70-75 percent of all participants, regardless of whether they were already on blood pressure medications or not, were likely to see a reduction in their blood pressure if they lowered the sodium in their diet.
This record-breaking funding marks a 73 percent growth in research awards over nine years.
The model may provide novel insights into RP59 disease mechanism that will guide future testing of therapeutic interventions.
Researchers have identified a gut-lung axis driven by intestinal antimicrobial peptide expression and mediated by the intestinal microbiota that is linked to lung injury in newborns.
Project TransTeam Evolution strives to improve outcomes for young children with high-intensity needs and their families through evidence-based practices and advance equity for children from diverse cultural, structural and socioeconomic backgrounds.
UAB researchers say this study underscores the significance of addressing food insecurity among college students, not only for its direct impact on BMI but also for its indirect effects on diet habits and psychological well-being.
The world’s first clinical trial of Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta found that patients treated with REBOA were more likely to die than those who did not undergo REBOA.
Cong’s research indicates the increased vulnerability of older adults to climate change impacts while also highlighting their resilience capacity in the face of disasters, offering valuable insights for policy development and disaster preparedness.
Analysis of a survey of 18,041 people in rural KwaZulu-Natal revealed a discrepancy between the ability of the South African health system to respond to the health needs of people with communicable diseases and the health needs of people with non-communicable diseases.
The Blazer Bridge Fund is intended to identify and assist in the development of promising ideas, discoveries, innovations and/or technologies from UAB faculty and staff that have commercial potential.
UAB researchers conducted a study in end-stage heart failure patients with cardiogenic shock that revealed that B-type natriuretic peptide levels were elevated in end-stage heart failure but did not predict clinical outcomes.
Lung-resident memory B cells produced during influenza are long-living immune cells that migrate to the lungs from draining lymph nodes and lie in wait as early responders that can quickly react to future infections. They are key sentinels against subsequent viral variants.
The modified mRNA — delivered after experimental heart attacks — transiently allows heart muscle cells to proliferate, leading to reduced infarct size and improved heart performance compared to untreated animals.
While preventive treatment with vigabatrin delayed the onset and prevalence of infantile spasms in TSC infants, it had no impact on focal seizures, drug-resistant epilepsy, or improvement of cognitive and behavioral scores at 24 months.
The study’s findings provide valuable insights into the role of diet composition in Type 2 diabetes management.
These results add an additional, mechanistic aspect to further explain how the decades-old blood pressure medication verapamil can preserve beta cell function in Type 1 diabetes patients by affecting the hormone insulin-like growth factor 1.
The new technology will allow for non-invasive assessments for dry eye disease and inform the development of new treatments.
Periodontal disease is one of the leading causes of tooth loss in adults and may be a risk factor in the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
In a mouse model, border-associated macrophages, not microglia, were essential for the neuroinflammation that precedes neurodegradation. Targeting this subset could be a disease-modifying therapy in neurodegenerative disease.
UAB is one of the seven institutions receiving multimillion renewal funding to advance its Cyber Corps program. The grant will support an integrated curriculum for training master’s students in both cybersecurity and artificial intelligence.
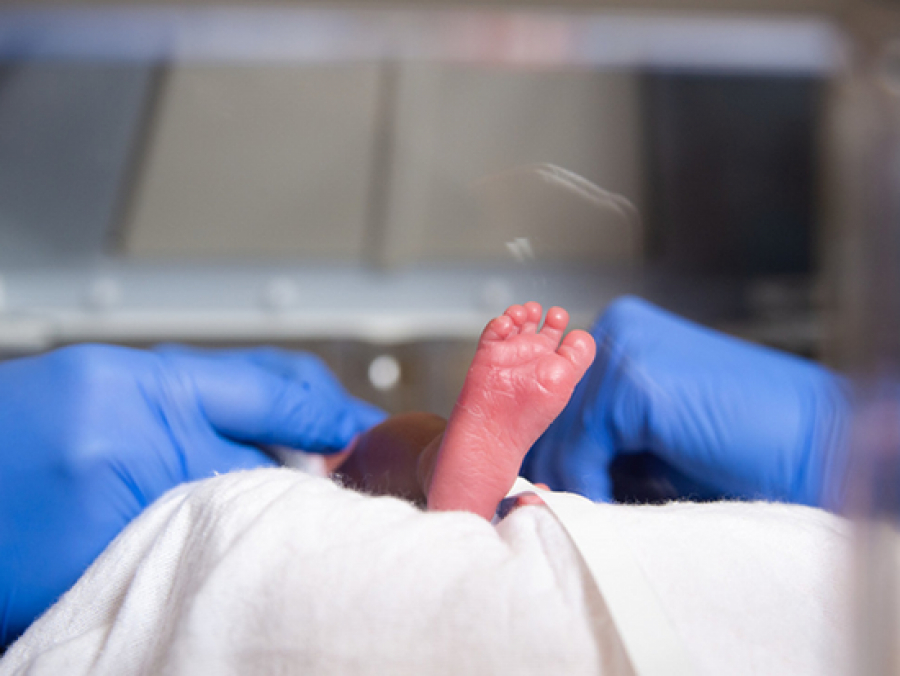
Published results from two UAB studies found the duration of intermittent hypoxemia events and the presence and persistence of a patent ductus arteriosus after birth are two novel risk factors of BPD-PH in preterm infants.
New research reveals how influencers’ words impact engagement in affiliate marketing on social media
The UAB study revealed that specific linguistic styles within influencer posts can enhance or diminish engagement with the content.
Earlier research suggests that the use of low-dose atropine drops plays a role in slowing the progression of myopia in children. However, new research co-led by experts in the UAB School of Optometry shows that may not be the case.
Because hypertension and uncontrolled blood pressure are major risk factors for heart disease and stroke, achieving equity in heart and brain health in the United States cannot be reached without paying attention to social determinants of health, a study shows.