Research & Innovation
UAB researchers have identified a critical vulnerability in quadruple-negative breast cancer, signaling pathway as a key driver of tumor growth and paving the way for targeted therapies that spare healthy cells.
The combo drug could mark a significant step forward in medical weight management — especially for patients struggling to lose weight through diet and exercise alone.
UAB’s Kathy Lu, Ph.D., will work in conjunction with other universities to lead a $7.5 million MURI project to optimize compositionally complex ceramics for hypersonics.
The American Heart Association’s PREVENT CVD risk equation is designed to help predict a person’s risk of a cardiovascular event during their lifetime.
The understanding of how macrophages regulate their response to toxic particles via two independent pathways could uncover therapeutic opportunities to quell inflammation.
Besides their normal role, pump overexpression confers drug resistance. Knowing the structure is a step to disabling the pumps with inhibitors.
UAB is a stronghold at finding patients for studies, but healthy controls were harder.
These findings implicate the Reelin signaling pathway as a potential therapeutic target for cocaine use disorder.
XMEA is a recessive, genetic disease that causes progressive muscle weakness.
Very-low-weight newborns need extra oxygen and can develop deadly bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Differences in gut fungi predict getting, or not getting, BPD.
UAB hopes to have a big impact on the health of adaptive sports athletes and expand successful injury prevention programs.
UAB’s Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine collaborates on a groundbreaking study published in Anesthesiology, introducing WISH, a novel tool to assess factors influencing health care workers’ well-being.
Jun has been elected to the American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering for his pioneering translational research.
UAB’s new Lunaphore COMET multiplex immunofluorescent platform can hyperplex up to 40 antibodies on a single pathology tissue sample.
Researchers identified that the dominant B cell epitope of Lachnospiraceae flagellins and the utilization of the flagellin peptide cytometric bead array can potentially advance the diagnosis and prognosis of Crohn’s disease.
New guidelines create clarity of language that will help advance mitochondria transfer and transplantation research for therapeutic innovations.
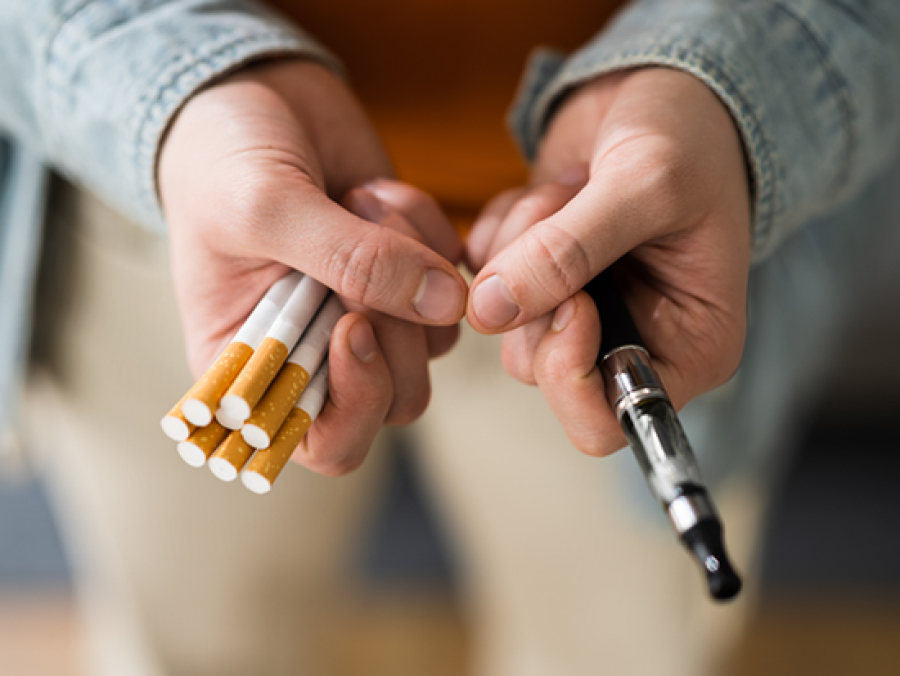
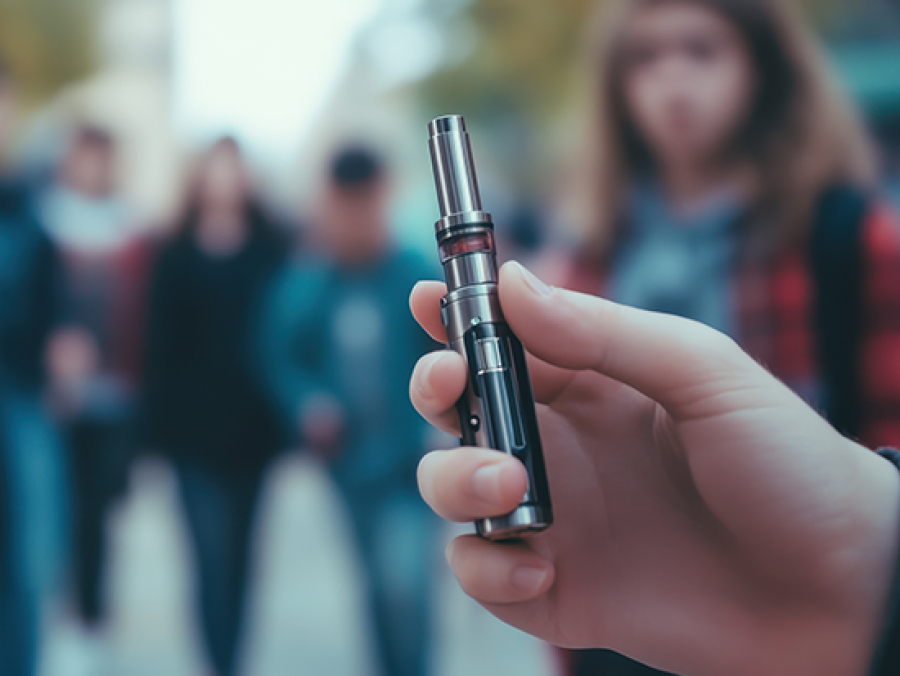
E-cigarette use among college-age students has drastically increased. UAB researchers studied the perception of health risks of e-cigarettes compared to traditional cigarettes.
The ability to alter protein binding can create tailored therapeutics with reduced side effects, sensitive diagnostic tools, targeted drug delivery and sustainable bioremediation.
UAB researchers reveal how managing cardiovascular risk factors can mitigate heart failure risk in Black individuals carrying the transthyretin V142I genetic variant.
The new AI tool can help counselors spot patterns in information that schools already collect that could be indicators of a higher risk of mental health conditions.
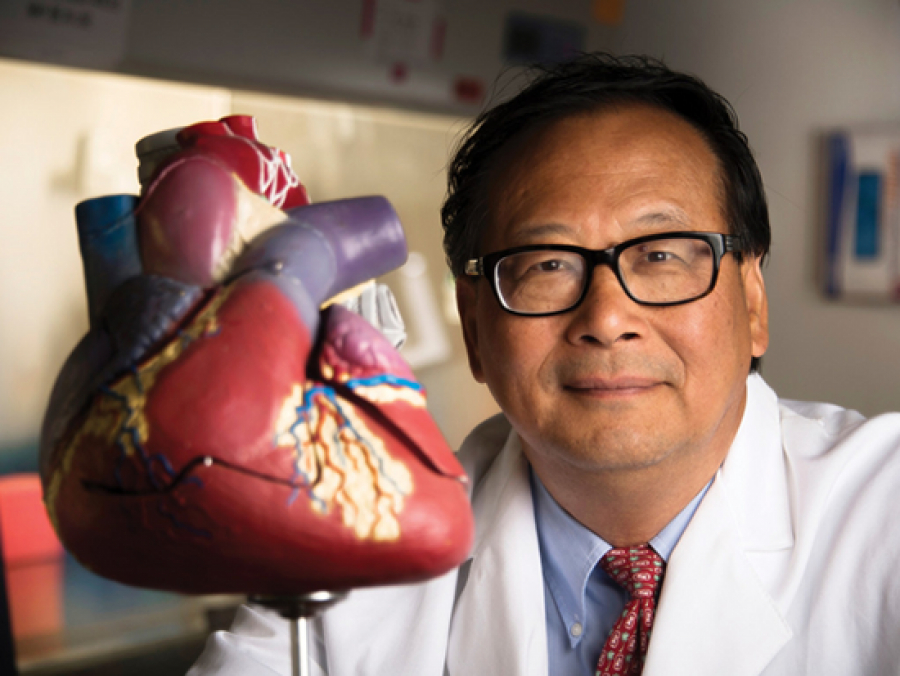
Injecting infarcted pig hearts with specially bioengineered cells significantly decreased the infarct area and improved heart function, showing possible clinical relevance.
Rachel Smith, Ph.D., is collaborating with researchers across UAB on the two-year project, which will focus on the intracranial neural networks responsible for major depressive symptoms in epilepsy patients.
The regulator HIF1α functions in a cancer-microenvironment that lacks oxygen, and it may be involved in resistance to immune checkpoint blockade therapy.
Results showed longer duration of hypertension is related to higher risk of stroke, higher average systolic blood pressure and a need for more classes of antihypertension medication.
Liou Sun’s research group will seek to understand how ceramides and growth hormone signaling contribute to healthier aging, providing meaningful insights to develop innovative therapies for age-related diseases.
There are no effective antivirals against BK polyomavirus in transplanted kidneys. A better understanding of its replication will offer new ways to protect those kidneys.
This study highlights how high-volume centers, where operators perform these procedures more frequently, achieve better outcomes, including lower 30-day mortality and reduced complication rates.
Heart failure is responsible for 13 percent of deaths worldwide, and half of patients die within 5 years. New therapies are needed.
UAB researchers uncover that interaction between proteins CD2:CD58 can be disrupted to mitigate the expression of genes and proteins that trigger HS pathogenesis.
UAB is combating youth tobacco use with its ninth annual award from the Alabama Department of Public Health.