Division of infectious diseases
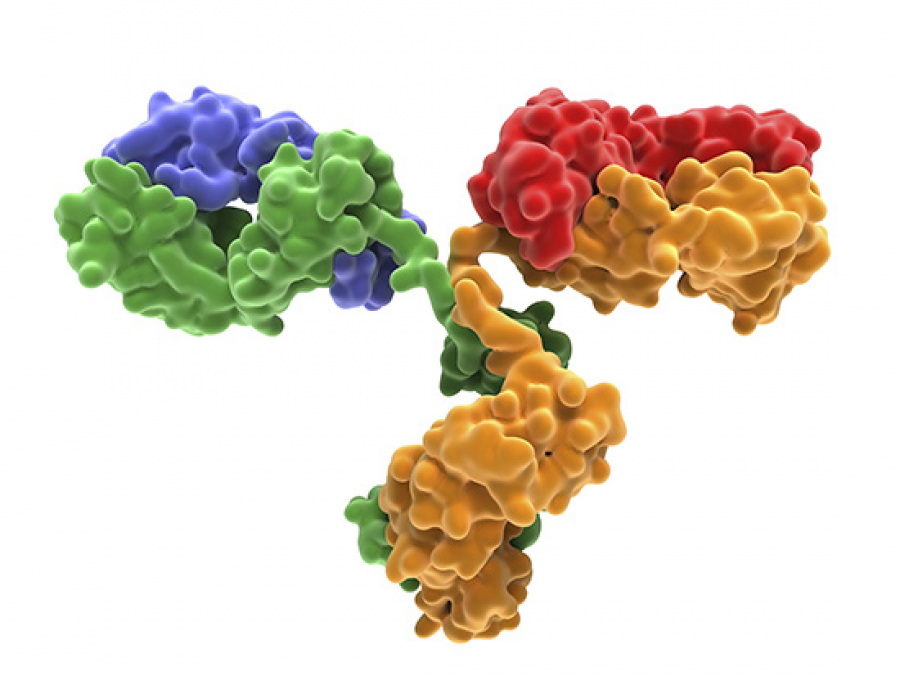
The monoclonal antibody cocktail is deliverable via a nasal dose, and it is also effective against SARS, MERS and several coronavirus cold viruses. The antibodies are engineered for long-acting effectiveness, potentially lasting a year or more when used in humans.

Many Americans are catching up on missed holiday plans, but should you go ahead and receive your booster shot to ensure the safety of yourself and others?

The effort led by UAB is projected to receive $17 million from NIH to support up to four years of patient follow-up.

Record $95 million Heersink lead gift to advance strategic growth and biomedical innovation.

Monoclonal antibody infusion is effective, but UAB doctors say getting the COVID-19 vaccine is the best way to prevent someone from being hospitalized because of COVID-19.

A comprehensive health-screening program in rural northern KwaZulu-Natal has found a high burden of undiagnosed or poorly controlled non-communicable diseases.
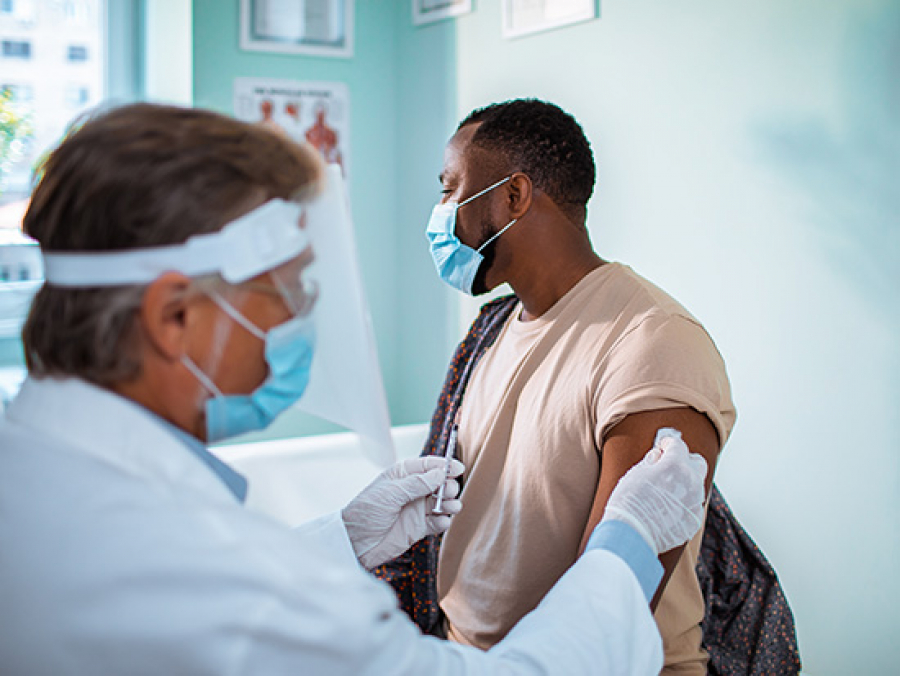
UAB experts explain some of the benefits of getting a COVID-19 vaccine.

Now that effective vaccines for COVID-19 have been developed and are being distributed to members of the public, it is key for folks to understand the benefits of the COVID-19 vaccines.
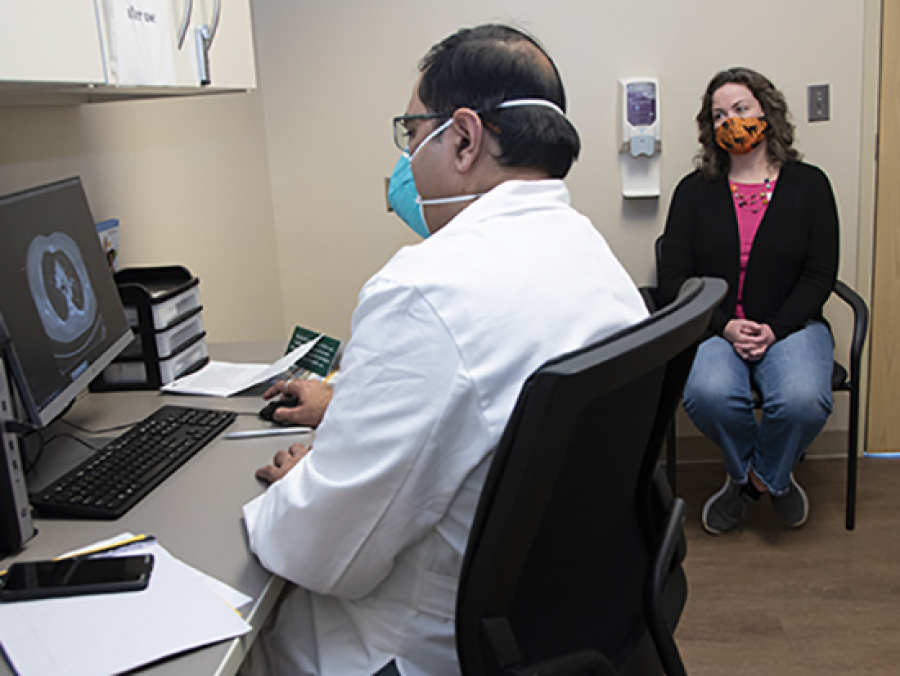
A new multidisciplinary program within UAB Medicine will help evaluate patients who have recovered from COVID-19 but are still experiencing symptoms and link them to the specialized care they need.

Visiting the pool or lake is synonymous with summer fun, but is it safe in a pandemic?

Cloth face masks must cover the mouth and nose and fit snugly against the side of the face.

The novel coronavirus can live on certain surfaces for up to two to three days.
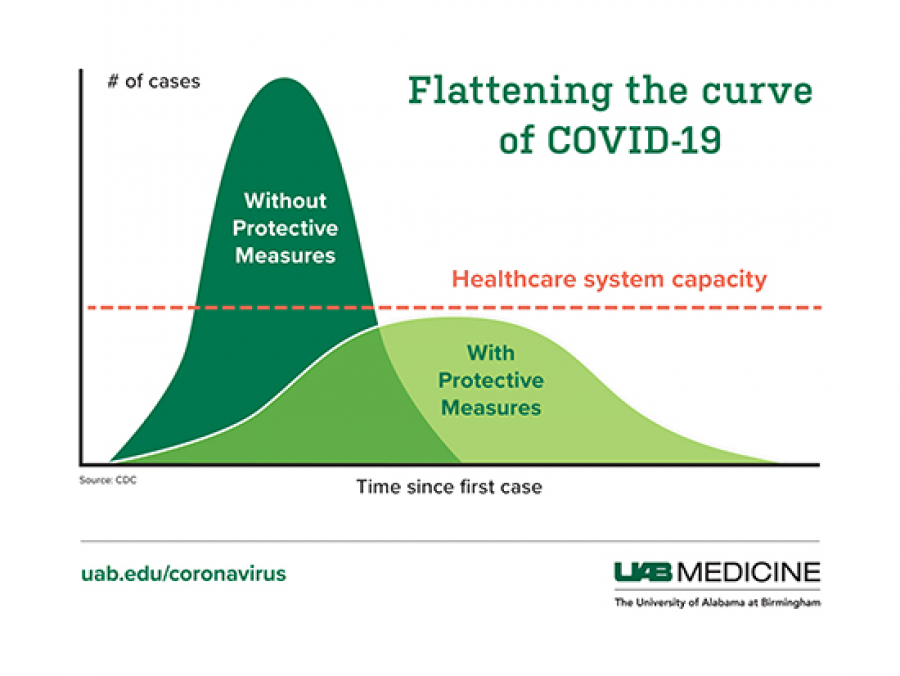
To stop a pandemic from growing, everyone must work together to “flatten the curve.”

Hear from UAB experts on the differences of COVID-19, flu, alleriges and colds.

These are some of the tips and tricks that could help you avoid the flu.
Research conducted at UAB is reaching the front lines of treatment of the novel coronavirus.
Researchers found that regular tenofovir gel users were associated with reduced risk of HSV-2 infection.
A UAB Infectious Diseases physician discusses bacteria found in food-borne illnesses and why you should wash your hands.
UAB researchers collaborated on a study showing a blood test for chlamydia might be valuable in screening infertile women for pregnancy outcomes.
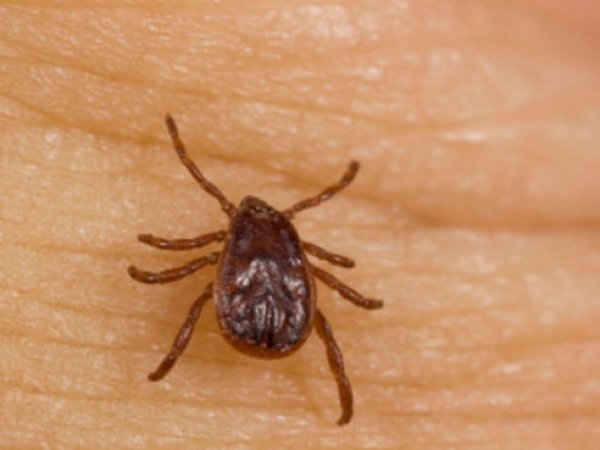

There’s ticks in them-there woods, and that means the possibility of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever, as one UAB patient recently discovered.
Page 2 of 2