Department of microbiology
Goal of this UAB-led service is transforming the global landscape of TB research through accelerated study of human TB tissue.

Indirect benefits could include how to lessen rejection of transplanted organs and damage to the transplanted tissue.

Cooper recently won the Albert Lasker Award, known as “America’s Nobel Prize,” given to the living person considered to have made the greatest contribution to medical science.

Lund is the fifth Distinguished Fellow from UAB named since 2019, a sign of the strength of immunology research at UAB.
The site-directed addition of a polymer on the antibody trastuzumab helped this cancer-fighting antibody cross the blood-brain barrier.
Vaccination of neonatal mice with group A Streptococcus promotes clonal expansion of B cells that produce antibody against GlcNAc. The association of reduced Type 1 diabetes risk after group A Streptococcus infection is dependent on these GlcNAc-specific B cells.
Tuberculosis, the world’s leading infectious disease killer, caused 1.6 million deaths in 2021, along with 10 million new cases of tuberculosis every year.

The Blazer Bridge Fund is intended to identify and assist in the development of promising ideas, discoveries, innovations and/or technologies from UAB faculty and staff that have commercial potential.
Lung-resident memory B cells produced during influenza are long-living immune cells that migrate to the lungs from draining lymph nodes and lie in wait as early responders that can quickly react to future infections. They are key sentinels against subsequent viral variants.
Periodontal disease is one of the leading causes of tooth loss in adults and may be a risk factor in the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
Knowledge of this previously unrecognized mechanism may aid therapy for patients with interleukin-6 signaling mutations and hyper-IgE Syndrome, or HIES.

These effector memory B cells appear poised for a rapid serum antibody response upon secondary challenge one year later, and evidence shows that the cells in this subset differ from all previously described memory B cell subsets.
Having a bacterial infection at the same time as COVID-19 is a greater risk factor for COVID-19 severity and mortality than previously described risk factors such as advanced age, male sex or various comorbidities.

The clinical trial focused on very young children, who have a more rapid loss of the pancreatic beta cells than do adolescents. The trial was constrained to a low-dose level, but showed safety and tolerability and reduced serum glucagon, a secondary outcome.
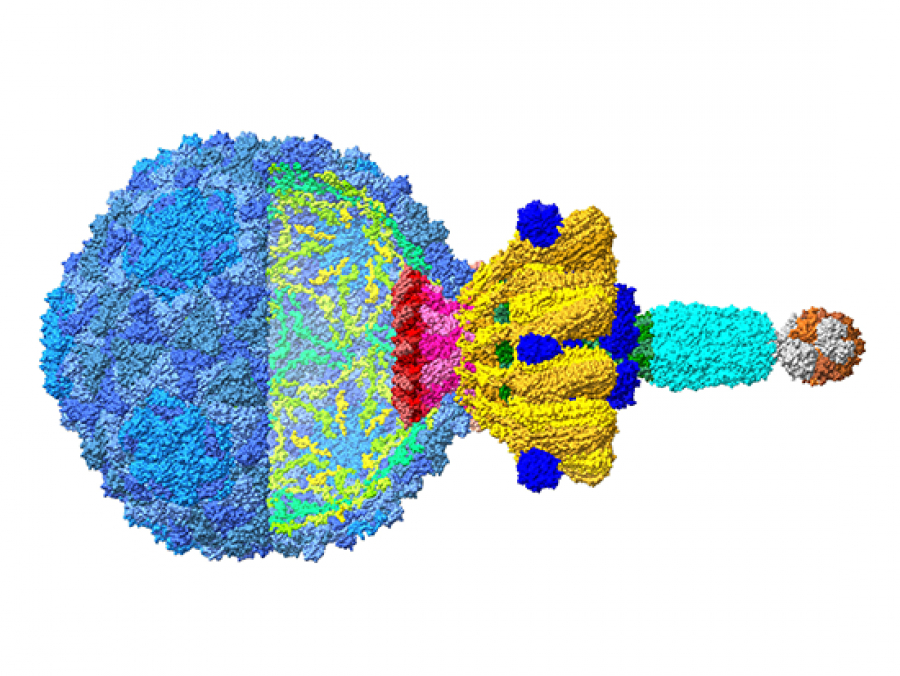
High-resolution knowledge of structure is a key link between viral biology and potential therapeutic use of the virus to quell bacterial infections.
A novel activity against hypothiocyanite has been found for an E. coli enzyme and homologs enzymes in Streptococcus, Staphylococcus and Bacteroides species, with implications for diseases like cystic fibrosis and inflammatory bowel disease.
X-ray crystallography revealed the structure of the HIV-1 matrix protein at 2.1 angstroms resolution, advancing understanding of key mechanisms of viral assembly.
The monoclonal antibody cocktail is deliverable via a nasal dose, and it is also effective against SARS, MERS and several coronavirus cold viruses. The antibodies are engineered for long-acting effectiveness, potentially lasting a year or more when used in humans.

Benefits of the blood pressure medication verapamil include delayed disease progression, lowered insulin requirements and preservation of some beta cell function.
In response to a viral infection, intrinsic IL-2 production by effector CD8 T cells affects IL-2 signaling, leading to different fates for two subsets of those cells — the one producing IL-2 and the one not producing IL-2.
Page 2 of 3