Research & Innovation
The National Institute on Drug Abuse award is designed to stimulate innovation and potentially transformative research from early stage investigators.
This investment marks a critical step forward in harnessing cutting-edge technology to revolutionize the accessibility and application of biomedical data science.
UAB researchers explore how polygenic risk scores can refine treatment decisions for patients with high blood pressure.
Results suggest that, rather than stimulating both sides of the brain using DBS, unilateral right DBS may avoid DBS-related declines in verbal fluency and response inhibition in patients with movement disorders like Parkinson’s disease.
UAB awarded more than $11 million to lead study on telehealth options for chronic disease management
A multisite study will compare the effectiveness of telehealth options in patients with a physical disability, Type 2 diabetes and one other chronic health condition.
By showing a critical role for sialylation in the biophysical properties of mucus and mucus transport, the study identifies a possible therapeutic target for the treatment of cystic fibrosis and other muco-obstructive diseases.
UAB researchers are pioneering five new projects as they continue making new discoveries and advancing science to benefit oral health locally and globally.
The NIH grant will support development of a BionanomatrixTM coating for an aneurysm-therapy flow diverter in the brain.
Blazer Bridge Fund provides financial support to innovative ideas and inventions by the UAB community, encouraging advanced discovery.
A cluster analysis in the Deep South showed that racial background significantly influences diabetes subtype distribution.
The study’s findings suggest a combination therapy could be a more effective and a safer approach to treating metastatic colorectal cancer.
Vohra is leading the Center for Additively Manufactured Complex Systems under Extremes at UAB in advancing understanding of 3D-printed materials when subjected to extremes of pressures, temperatures and high-velocity impacts.
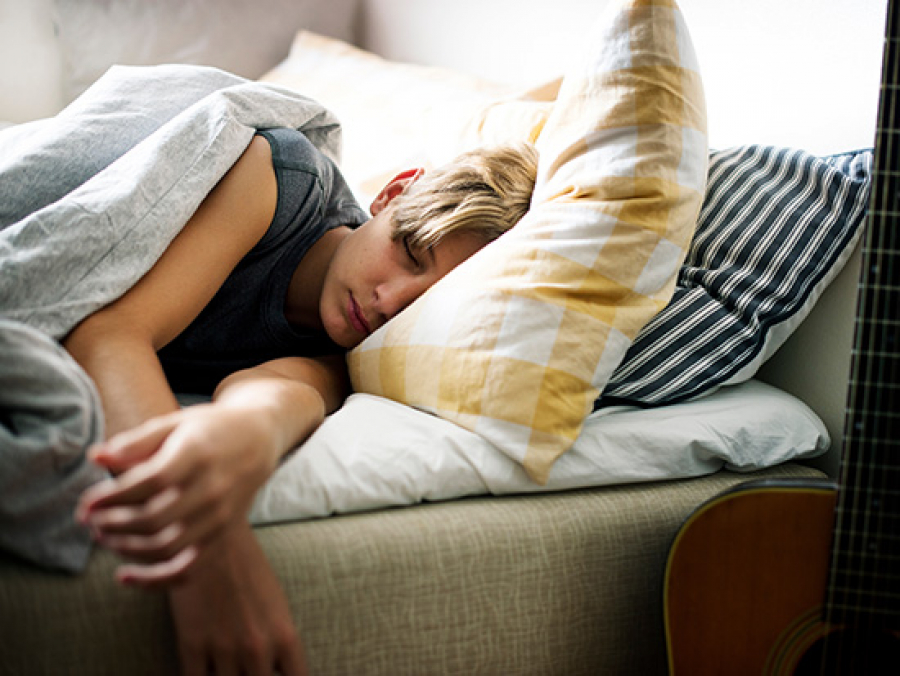
A recent study by UAB researchers showed that teenagers with higher levels of adiposity have more cognitive impact from poor sleep compared to teenagers with a healthy weight.
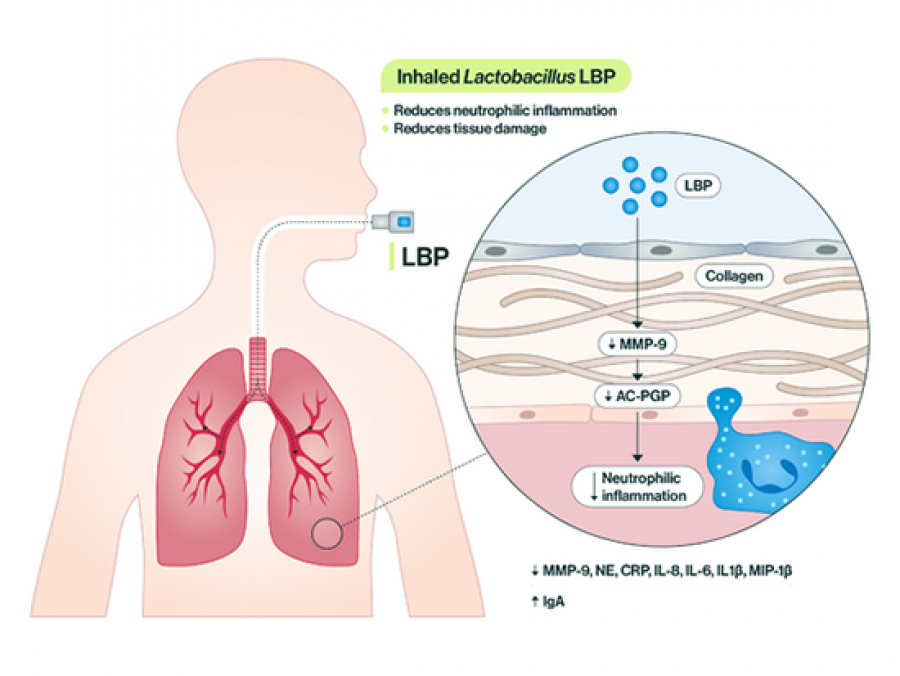
This live biotherapeutic product, tested in mouse models, shows promise in addressing common pathways of lung disease progression.
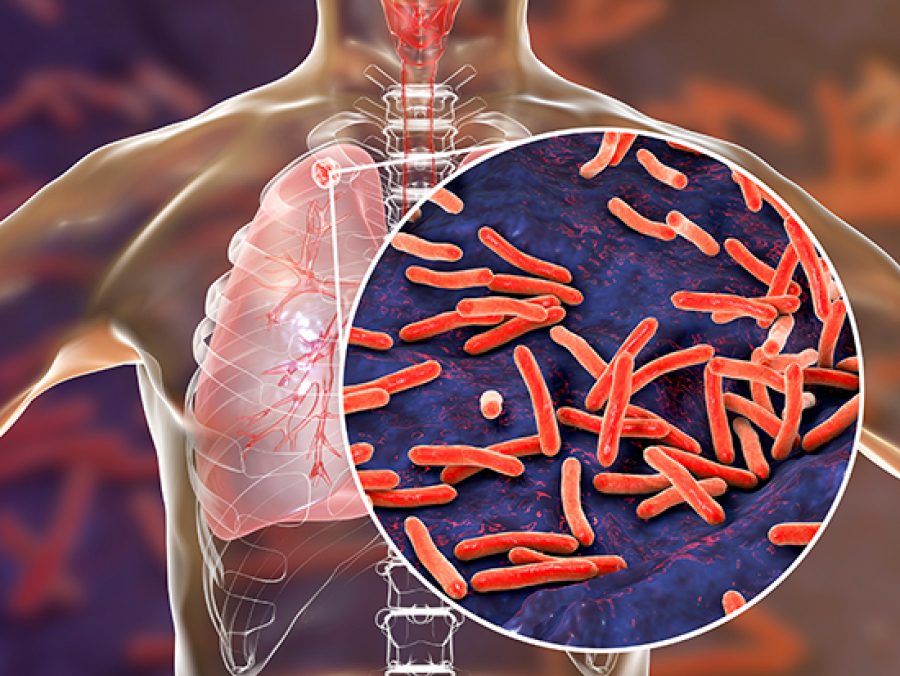
Goal of this UAB-led service is transforming the global landscape of TB research through accelerated study of human TB tissue.
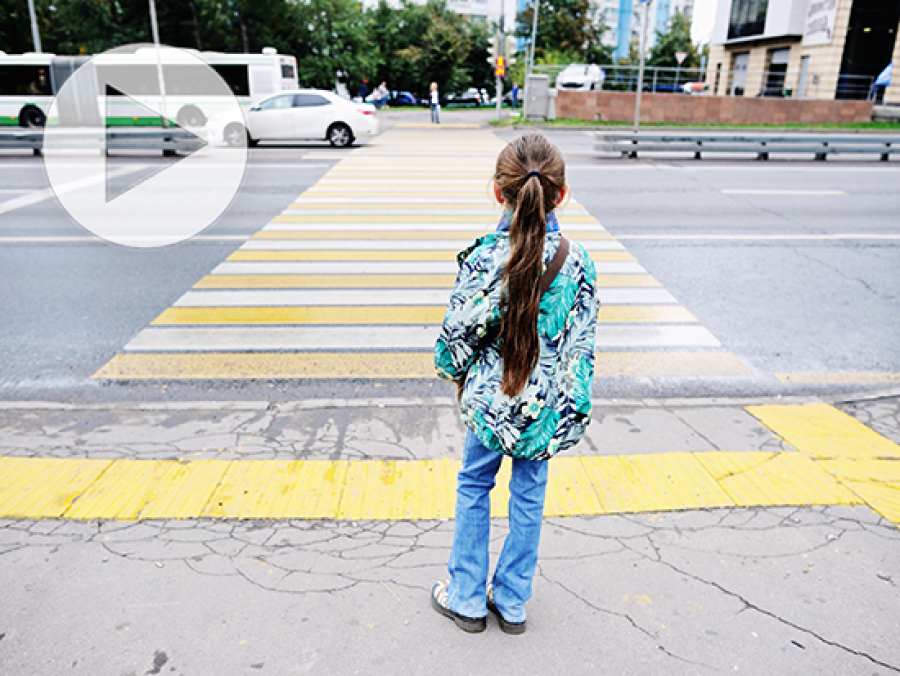
Study looks at how much virtual training children could use to develop adult street crossing competency and what might help children acquire that competency earlier.
Researchers at UAB shed light on the link between genetic variants and cardiovascular risk factors in determining heart health.
The findings suggest disparate effects of phased COVID-19 vaccine rollout on mental health across U.S. populations.
This finding suggests that therapy to remodel synapses could help memory in old age and dementia patients.
The novel drug TIX100 functions differently from any approved diabetes drug to promote proper islet cell function.
Fobian developed Retraining and Control Therapy, or ReACT, to help patients with functional neurological disorder, or FND, which affects an estimated 300,000 Americans.
Researchers at UAB reveal the impact of transthyretin protein levels on heart disease risk.
The study reveals how political savvy and community engagement in micro labor markets can boost earnings and counter financial marginalization.
States such as Mississippi and Louisiana were found to have the highest rates, while the lowest rates were found in the Northeast, followed by states in the West and Midwest.
UAB expert studies head impact and helmet protection for equestrian riders.
These findings in zebrafish and human heart muscle cells have clinical implications for patients with atrial fibrillation.
The NSF awarded $77.8 million to 14 projects, including the Interdisciplinary Program of Advancing Climate Extreme Resilience in Soybean, or iPACERS.
Research from the centers will help drive new knowledge and foster positive and lasting societal benefits.
This past June, through a competitive review process, the NIH renewed their five-year grant to continue UAB’s Center for AIDS Research pivotal work.