Latest from NORC

New research presented by University of Alabama at Birmingham researchers shows that a 2.4mg dose of the obesity drug semaglutide can reduce the risk of Type 2 diabetes, or T2D, by 60 percent.

Alabama, a state with many counties in the United States Diabetes Belt, saw an increase in new-onset Type 2 diabetes among youth during the COVID-19 pandemic. Results published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism showed the significant increase and indicated that Medicaid enrollees and males were disproportionately affected by the disease.

Aging is a fact of life. Each year, a person finds themselves hitting new age milestones, decades and life seasons, all of which bring about physical, emotional and cognitive changes. In looking at aging, overwhelming evidence shows healthy lifestyle habits can improve a person’s well-being, ultimately making a difference in their quality of life throughout their lifespan.

High blood pressure — hypertension — is the leading underlying cause of death worldwide. More than 1.25 billion people have hypertension, including more than 100 million Americans. Most people worldwide eat more salt than recommended, too. Is there a connection?

We are excited to announce a joint pilot with Microbiology, please see below for the link to the Microbiology/Nutritional & Obesity Research Center (NORC) Pilot grant RFA and the REDCAP portal to submit the pilot project. The pilot grant will be for $50,000 and is for a collaboration between a faculty member in Microbiology and a member of the NORC. Pilot projects are meant to generate preliminary data that can be used in competitive grant applications to the NIH, NSF or other extramural funding agencies.

In a new supplement to the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, University of Alabama at Birmingham researchers have identified complex contributors to obesity and obesity-related health disparities and propose strategies for improving the well-being of populations impacted by these disparities.

Camille Worthington, PhD, RDN, LDN has been selected as this year’s Named New Investigator for the UAB Nutrition Obesity Research Center (NORC). The center leadership selects from among funded pilot/feasibility recipients and then receives approval from the UAB NORC External Advisory Committee prior to formally making the appointment.

A novel therapy developed at the University of Alabama at Birmingham ameliorates obesity and Type 2 diabetes in mice fed a high-fat diet. The therapy acts through sustained release of nitric oxide, a gaseous signaling chemical whose most important function in the body is relaxing the inner muscles of blood vessels.
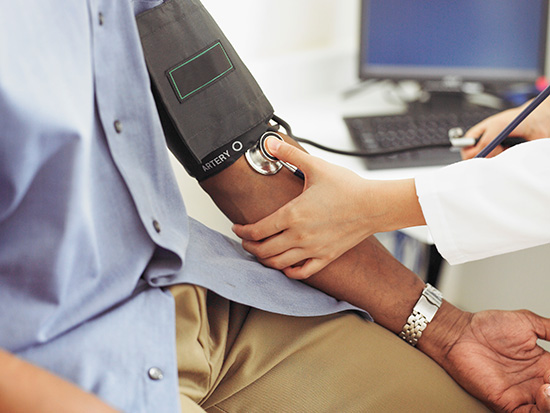
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, high blood pressure was a primary or contributing cause of more than a half million deaths in the United States in 2019. Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham have launched a study in a subset of patients — obese individuals who experience high blood pressure at nighttime.