Clinical History
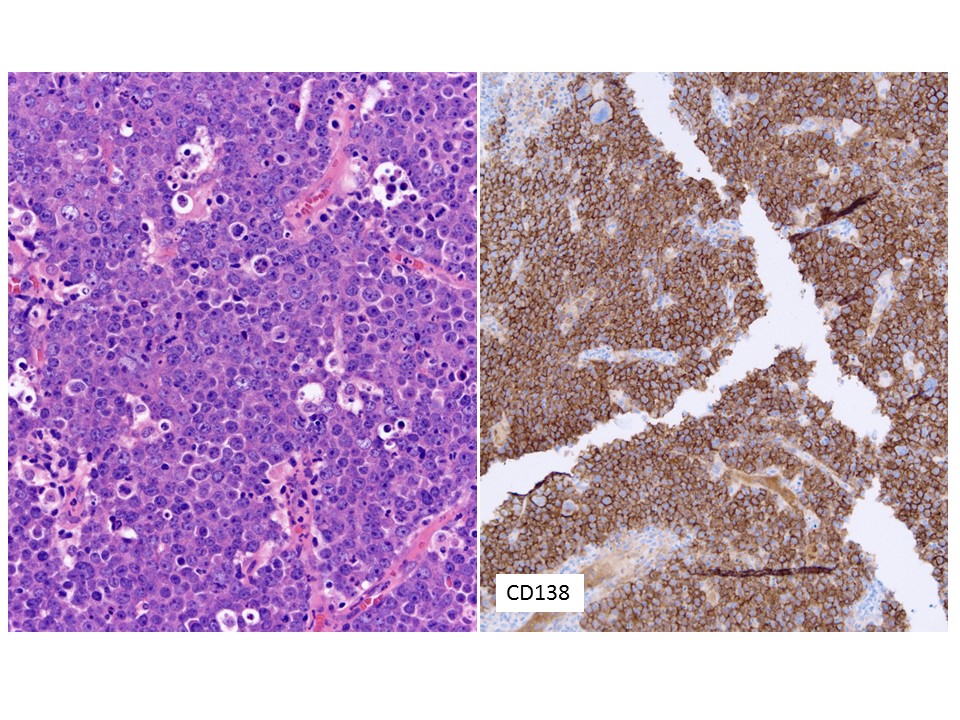
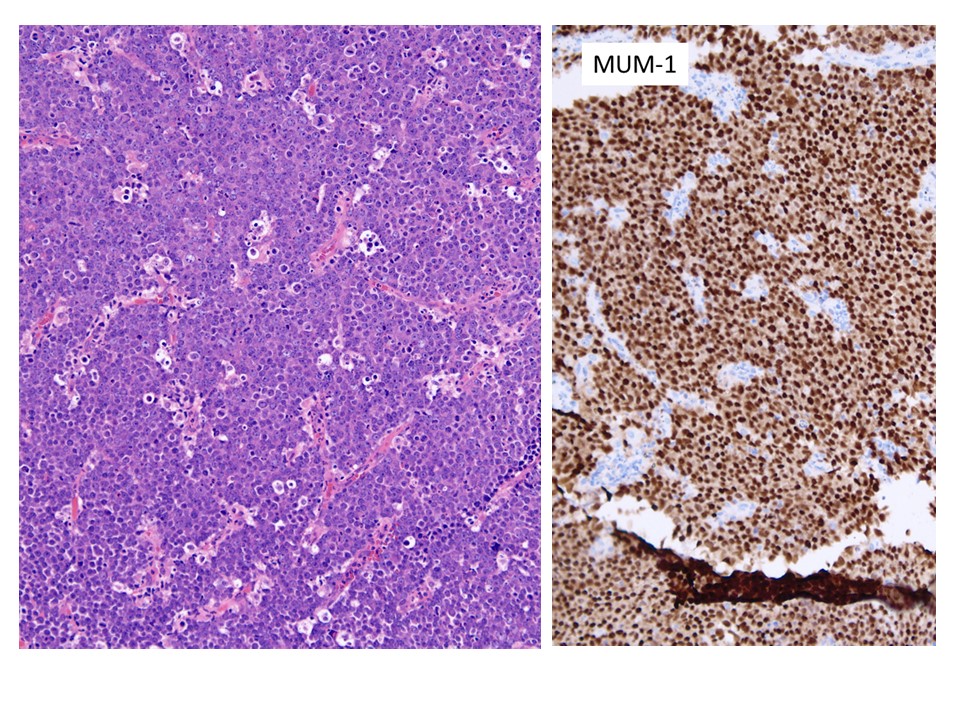
40 year old female with pelvic mass and friable cervix, biopsy was performed at OSH. Neoplastic cells positive for CD20+, CD138+, MUM-1+, CD56+, EBER-/+, CD30-, HIV-. C-MYC deletion.Choose the Correct Diagnosis:
- Plasmablastic lymphoma
- Plasmacytoma / myeloma
- Large B-cell lymphoma
- Reactive/EBV-related neoplasm
Answer: B. Plasmacytoma / myeloma
Discussion:
IHC and molecular studies support a plasmablastic malignancy. The differential consideration include a plasmablastic lymphoma versus anaplastic plasma cell tumor/plasmacytoma. Weak EBV and CD56 expression favor plasmablastic malignancy/ plasmacytoma over plasmablastic lymphoma. However, there is a considerable overlap on the diagnostic criteria and ancillary studies. Need bone survey, bone marrow biopsy, serum protein electrophoresis, free light chain ratio (FLC), urine protein electrophoresis for accurate classification.
|
Plasmablastic Lymphoma |
Plasmablastic myeloma/plasmacytoma |
|
Extranodal, head-neck, oral cavity and GI. Other rare sites GU, skin & bone etc. |
Medullary, extramedullary, soft-tissue and parenchymal |
|
HIV+ (most cases) of immune deficient |
HIV- |
|
EBV (60-75%) |
EBV- |
|
CD138+, MUM1+, CD20-, CD79a (40%), PAX5-/+, CD56 (25%), CD10(10%), BCL-6-, cIg+ (k/l) |
CD138+, CD56+, CD117+, CD20-, CD70a- cIg+ (kappa/lambda) |
|
IgH rearrangement+, complex karyotype, c-MYC translocation (50%), c-MYC protein expression |
|
Contributed by Vishnu Reddy, M.D. Interim Division Director, Anatomic Pathology and Neuropathology; Professor, Laboratory Medicine, UAB Department of Pathology