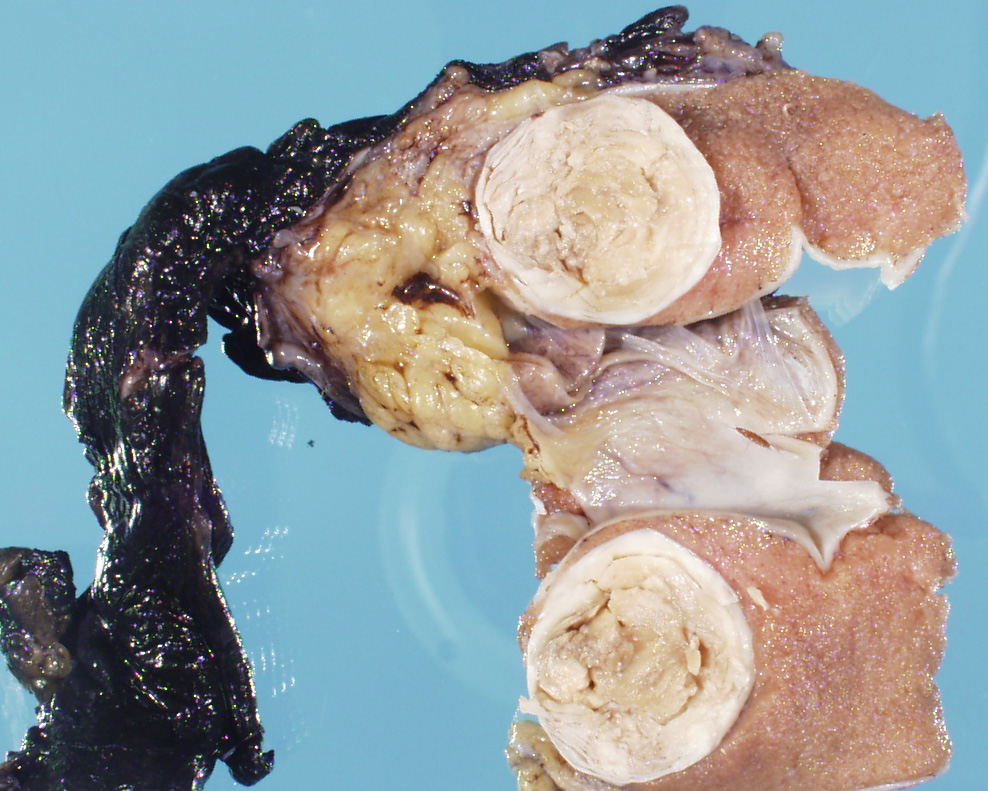
Clinical History:
A 13-year-old male undergoes orchiectomy for a testicular mass. Ultrasound shows an onion-skin like pattern to the mass. Histology show a squamous cyst with keratin debris. You want to decide between a prepubertal (benign) and postpubertal (malignant) teratoma. What is the next molecular study you will perform?
A. 12p amplification
B. Isochromosome 3p
C. EWSR1 translocation
D. Xp11.2 translocation
E. MET gene mutation
The answer is “A.” 12p amplification
Discussion:
The gross photo shows an epidermal inclusion cyst of the testis, which is benign and should lack 12p amplification. You should also not see germ cell neoplasia in situ (GCNIS). Teratomas occurring in prepubertal patients lack GCNIS and 12p amplification. It is now recognized that pre-pubertal-type tumors can sometimes be found in postpubertal patients. Ref: Williamson SR, Delahunt B, Magi-Galluzzi C, Algaba F, Egevad L, Ulbright TM, Tickoo SK, Srigley JR, Epstein JI, Berney DM; Members of the ISUP Testicular Tumour Panel. The World Health Organization 2016 classification of testicular germ cell tumours: a review and update from the International Society of Urological Pathology Testis Consultation Panel. Histopathology. 2017 Feb;70(3):335-346.
Case contributed by Jennifer Gordestsky, M.D., Associate Professor, Anatomic Pathology