Case History
This is a 60-year-old male with pancytopenia, weight loss, and a lesion of his right arm.
What is the diagnosis?
- Melanoma
- Leukemia cutis
- CTCL
- BPDC Neoplasm
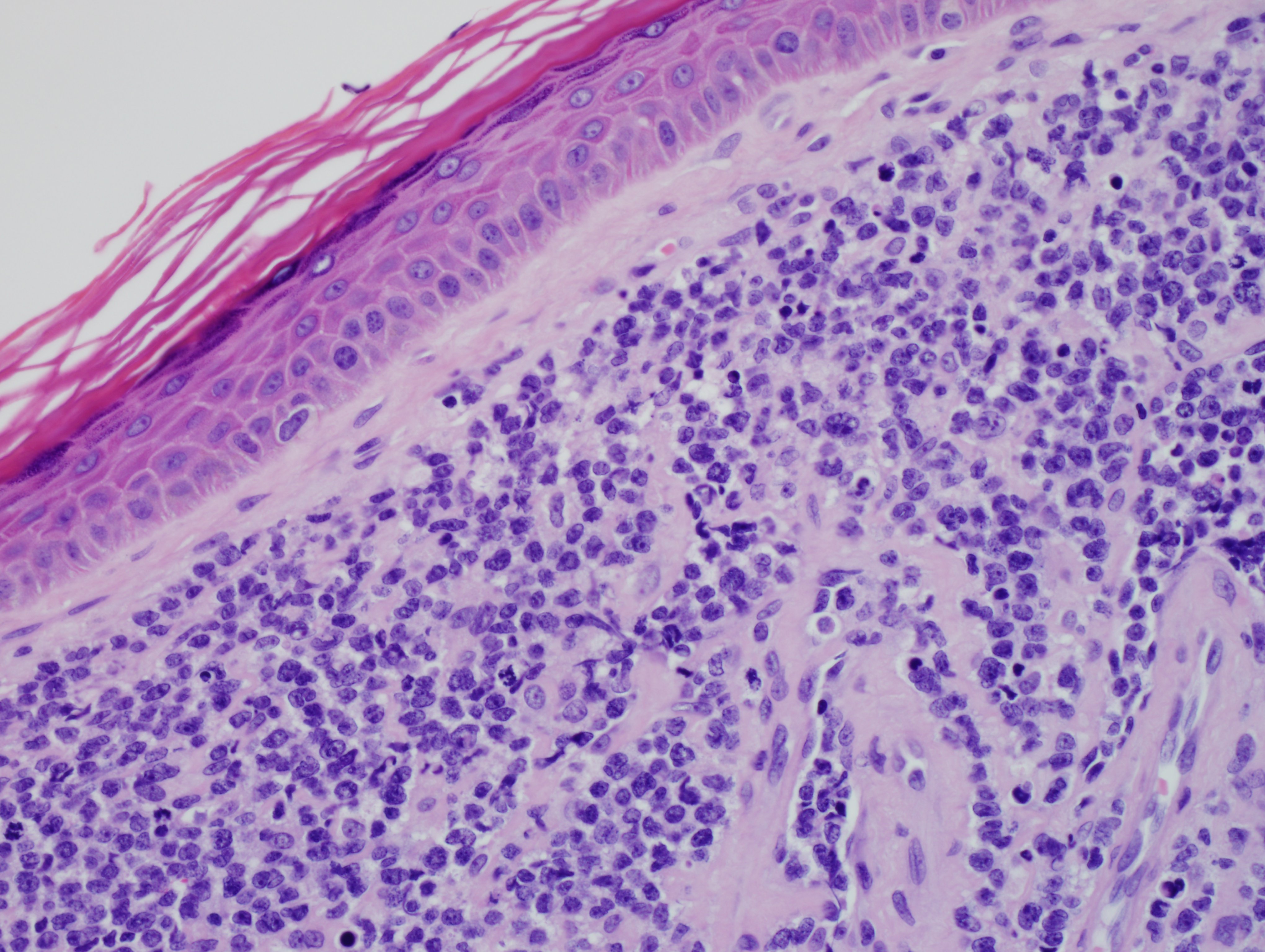
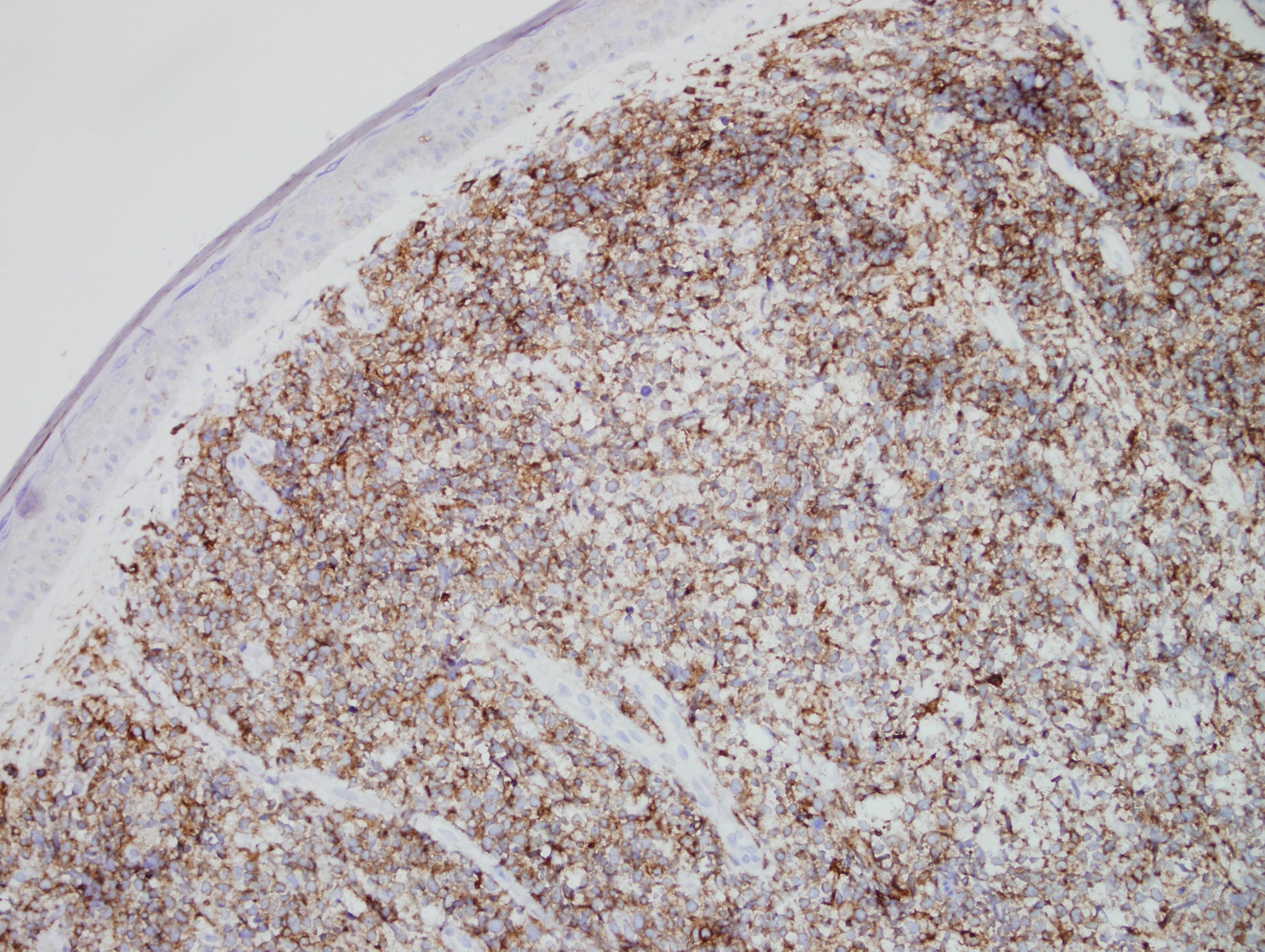
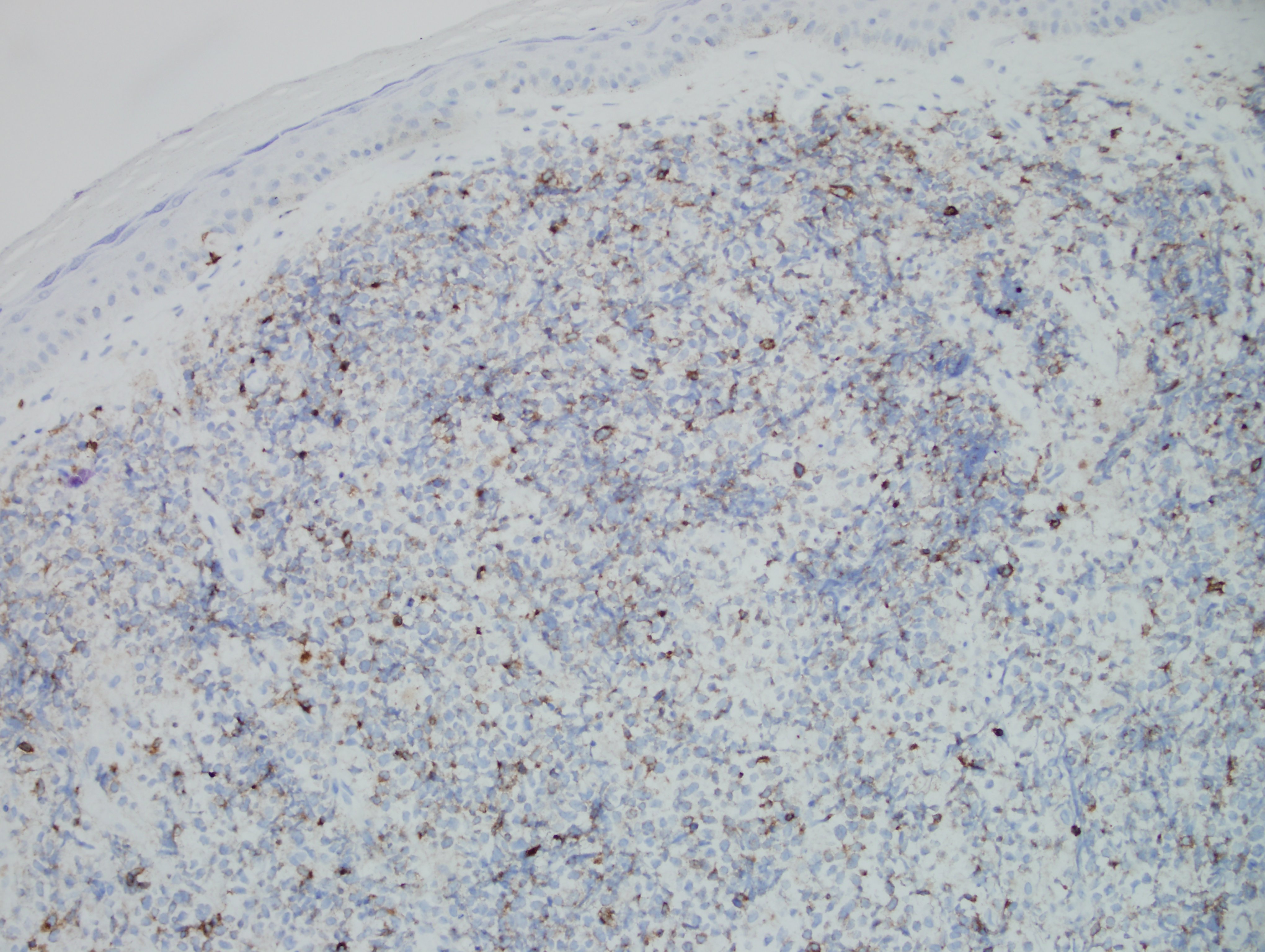
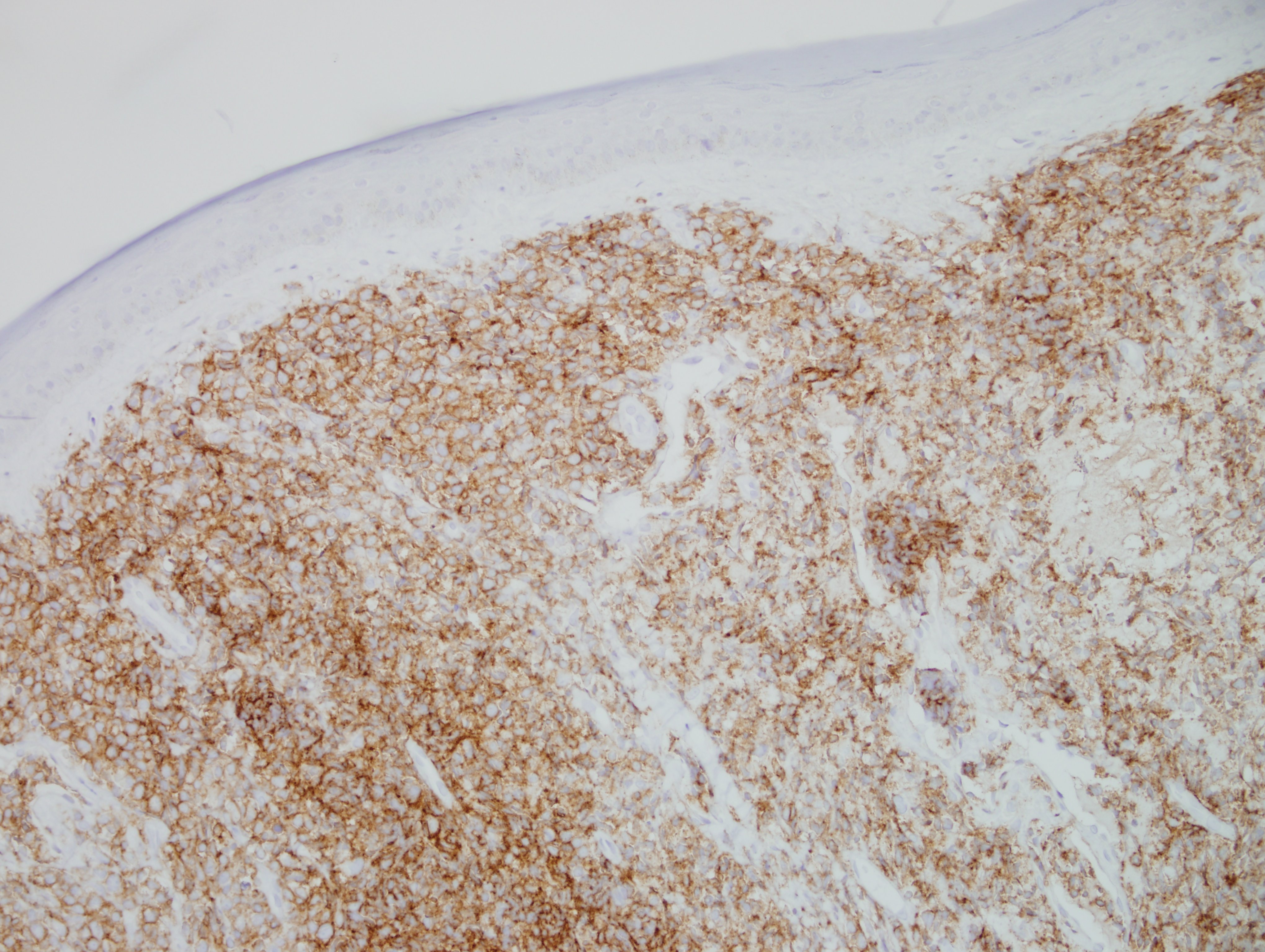
Answer: D. BPDC Neoplasm
Blasticplasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN) is a very aggressive hematodermic neoplasm with poor prognosis. Most patients affected are in the sixth to seventh decade and it has a male preponderance, with the male/female ratio being approximately 3:1. The etiology is unknown; however, strong association with myelodysplasia and myeloid neoplasms is known. BPDCN has a predilection for the skin and a high percentage of patients with bone marrow and peripheral blood involvement. Moreover, lymph node involvement occurs nearly 50% of the time. Patients may present with leukocytosis or cytopenias, with thrombocytopenia being the most common. Hepatosplenomegaly may also be seen.
Morphologically, BPDCN is characterized by a diffuse infiltrate of blastoid, monomorphic and medium-sized cells with scant cytoplasm, irregular nuclei, fine chromatin, and nucleoli. Mitoses are typically present and necrosis is usually absent. With cutaneous manifestations, epidermotropism is not observed. Tumor cells typically express CD4, CD7+/-, CD56, CD123, CD303, TCL1, and CD43. Very rarely, CD56 can be negative. CD33, CD79a, BCL2, and BCL6 can also be expressed. T-cell and B-cell receptor genes are usually germline. Several recurrent chromosomal abnormalities have been noted, such as 5q21/5q34, 12p13, and 13q13-21.
References: Swerdlow, S.H. (2017). Who classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. In WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues (pp. 173-177). Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer.