Case History
A 21-year-old pregnant female presents at term gestation in labor. She has had limited prenatal care this pregnancy. The subsequently delivered neonate shows a desquamating maculopapular rash of the soles.
Given the placental histology, which infection do you suspect?
A) Herpes Simplex Virus
B) Cytomegalovirus
C) Toxoplasma
D) Syphilis
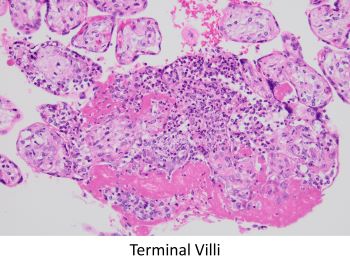
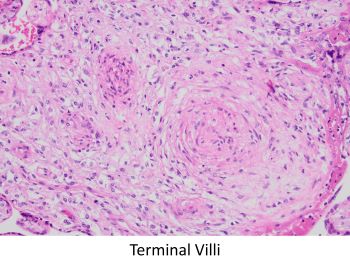
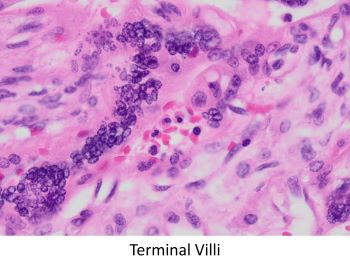
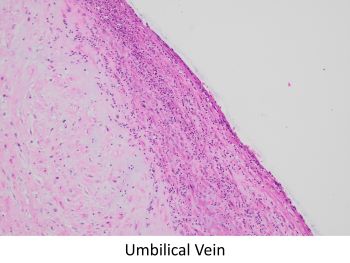
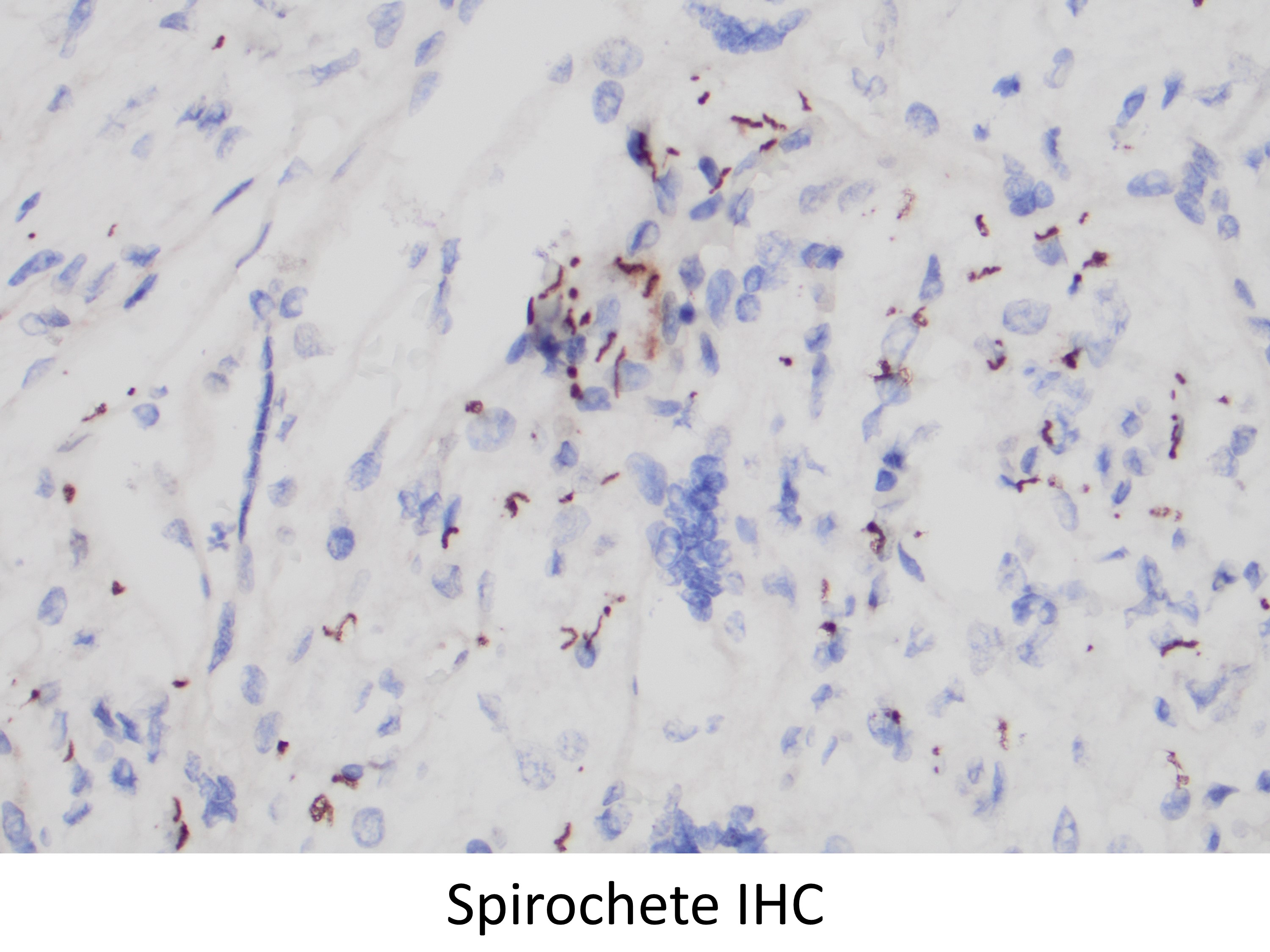
The clinical history of a desquamating rash involving the soles raises the possibility of an infectious agent, particularly syphilis. Placental histology, in this case, shows immature villi with prominent Hofbauer cells. Villous vessels are markedly thickened to the point of obliteration. There is also acute villitis/intervillositis/perivillitis. These features together are highly suggestive of syphilis. Immunohistochemical staining for spirochetes was positive. Additional features seen in this case are umbilical phlebitis and increased red blood cell precursors in fetal circulation. Although not appreciated in this case, severe necrotizing funisitis is seen in about half of cases of syphilitic placentitis.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is usually associated with a lymphoplasmacytic villitis and only rarely involves the umbilical cord. Herpes simplex virus (HSV) may show a lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate of the membranes and umbilical cord, with only rare involvement of villi. Both CMV and HSV may show cells with viral cytopathic changes. Toxoplasma organisms can be seen in the amnion, amniochorion stroma, and in Hofbauer cells. Other findings include villous enlargement with prominent Hofbauer cells and lymphohistiocytic villitis or granulomatous villitis if the Toxoplasma cysts have ruptured.