Case History
A 43-year-old female presents with chronic unexplained diarrhea. Colonoscopy shows normal mucosa. A random colon biopsy is taken (shown below).
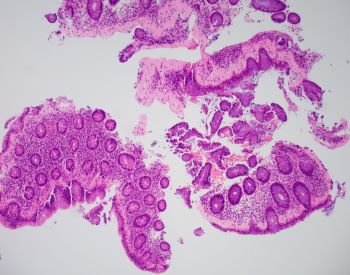
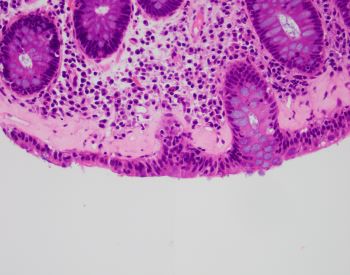
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Amyloid
B. Ischemic colitis
C. Collagenous colitis
D. Scleroderma
The most likely diagnosis is collagenous colitis. Clinical presentation typically consists of chronic unexplained diarrhea with or without abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss. A colonoscopy shows normal colonic mucosa or mild nonspecific changes. Collagenous colitis is a type of microscopic colitis. Histologic sections show a thickened subepithelial collagen band (>10 μm) with inflammatory cell entrapment and capillary proliferation. A trichrome special stain can highlight the collagen deposition. The surface epithelium may show reactive changes or a mild increase in intraepithelial lymphocytes. The other type of microscopic colitis is lymphocytic colitis, and would show more prominent intraepithelial lymphocytes than collagen deposition. The differential diagnosis may include amyloid deposition. Amyloidosis sometimes shows subepitheilal deposition, however most often involves blood vessels. A congo red special stain would highlight amyloid and inflammation would not be increased. Ischemic colitis shows diffuse lamina propria hyalinization and scleroderma involving the gastrointestinal tract shows fibrosis of the muscularis propria.
Case contributed by Anne Prater, D.O., Surgical Pathology Fellow, UAB Department of Pathology