Case History
IUFD at 23 weeks.
What is the most likely association with these placental findings?
A. Maternal anti-fetal reaction
B. Neonatal long bone destruction
C. Soil-borne fungus
D. Undercooked meat consumption
Correct Answer: D. Undercooked meat consumption
Discussion:
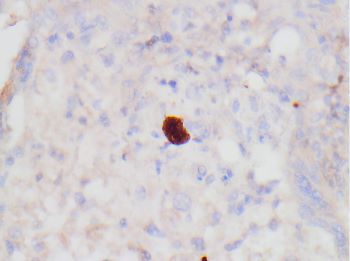
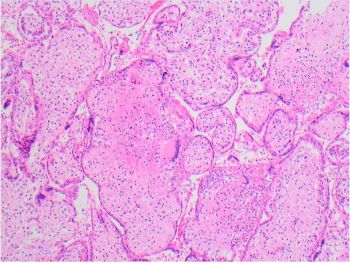
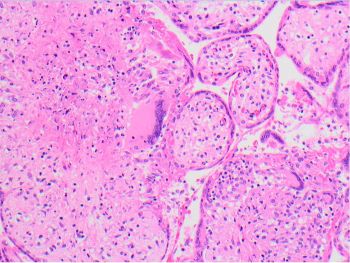
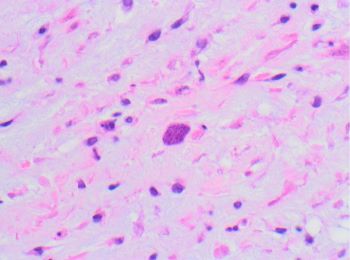
This is a case of congenital Toxoplasma gondii infection in the placenta. A dense chronic villitis consists mainly of lymphocytes and histiocytes with a prominent granulomatous component containing Langhans giant cells. The inflammatory infiltrate in T. gondii infection may also contain plasma cells, but in this case did not. T. gondii cysts are most conspicuous within the amniochorion and Wharton’s jelly of the umbilical cord and may be seen on H&E, PAS stain, or immunostain. Organisms within the villi may be challenging to identify on routine H&E stain, but immunostain and PAS can highlight them, as pictured in this case. A T. gondii cyst is pictured on H&E stain within the Wharton’s jelly of the umbilical cord.
T. gondii, a coccidian protozoan, is an obligate intracellular parasite. Cats are the definitive hosts, but humans and other mammals can also be infected. Human infection occurs from ingestion of water or food contaminated by cat feces, or via the consumption of tissue cysts in undercooked meat or eggs. Infection of the fetus occurs via transplacental transfer of the organism during a primary infection of the mother. About half of infected mothers will transmit the infection to their fetus. Early gestation transmission is less common than later gestation, but is more severe and may lead to miscarriage or stillbirth.
The other answer choices are incorrect. Coccidioides immitis, also known as valley fever, is caused by a soil-borne fungus endemic to the southwestern US and Mexico. It can infect the placenta, causing a chronic villitis with large fungal spherules accompanied by a foreign body giant cell reaction, but only rarely infects the fetus. Toxoplasmosis is caused by maternal immune reaction to the offending organism, not by a maternal reaction to fetal antigens. Congenital syphilis can cause long bone destruction in the neonate, but this not a typical feature of congenital toxoplasmosis.
Reference:
Heerema-McKenney A. Defense and infection of the human placenta. APMIS. 2018 Jul;126(7):570-588.
Case contributed by: Virginia Duncan, M.D., Associate Professor, Anatomic Pathology, Perinatal Section Head, UAB Pathology