Displaying items by tag: department of epidemiology
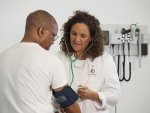
The study found that 70-75 percent of all participants, regardless of whether they were already on blood pressure medications or not, were likely to see a reduction in their blood pressure if they lowered the sodium in their diet.
Tagged under
Since 1985, the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults study has examined the factors that contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease to better understand the natural history of cardiovascular disease over the adult life course.
Tagged under
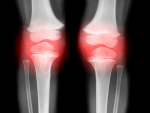
$46 million awarded by NIH to UAB and partners allows researchers to continue following participants enrolled in the national Multicenter Osteoarthritis Study.
Tagged under
Despite fewer drivers on the roads and fewer injuries per accident, fatal crashes in Alabama increased by 26 percent over the three years from 2020 through 2022.
Tagged under
Tagged under
The federal mandate, which was announced in 2011 and implemented in 2014, limited acetaminophen to 325 milligrams per opioid-acetaminophen combination pill. Acetaminophen is toxic to livers at high doses.
Tagged under
Published results show that higher cardiorespiratory fitness in early adulthood produces a lower risk of all-cause mortality later in life. Additionally, retaining good cardiorespiratory fitness through midlife reduces the later risk of death.
Tagged under
The clinical trial focused on very young children, who have a more rapid loss of the pancreatic beta cells than do adolescents. The trial was constrained to a low-dose level, but showed safety and tolerability and reduced serum glucagon, a secondary outcome.
Tagged under
The first large multi-ancestry genetics study of osteoarthritis, or OA, has found 10 novel OA-associated genetic loci, and results showed some of the OA-associated regions are robustly found in every population ancestry studied.
Tagged under
- release
- school of medicine
- department of medicine
- department of surgery
- department of cell developmental and integrative biology
- division of pulmonary allergy and critical care medicine
- school of public health
- department of epidemiology
- department of genetics
- department of biostatistics
- public health research
Owsley and McGwin will lead three data collection sites in the collection of data to inform machine learning approaches to provide critical insights into the endemic condition Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Tagged under
UAB is participating in a multi-center clinical trial that will dig deeper into the connection between hypertension and salt intake.
Tagged under
This is the first study to examine mistreatment from patients across the entire clinical team and to examine the experience of gender and sexual minorities.
Tagged under
Gargya Malla, M.D., Ph.D., used the UAB REGARDS study to evaluate the effect of living in a disadvantaged area on heart failure risk. She was awarded second place in a data challenge hosted by the American Heart Association® and the Association of Black Cardiologists.
Tagged under
Vacuuming, mopping, walking a pet or playing catch may be enough activity to avoid a stroke, according to a national study published in JAMA Network Online.
Tagged under
Kidney failure experts recommend new tool that eliminates race as a determining factor for diagnosis
New findings published in the Journal of the American Medical Association show an eGFR equation that excludes race as a coefficient and includes creatine and cystatin C measurements could demonstrate racial differences in the risk of kidney failure requiring dialysis.
Tagged under
The virtual webinar will explore the importance and helpful tools that entail accuracy and transparency of pandemic news.
Consortium led by UAB researchers in the UAB Heersink School of Medicine and School of Public Health received additional funding to further study chronic hypertension and preeclampsia epigenetics participants enrolled in the CHAP trial.
Tagged under
A UAB epidemiology expert will evaluate genetic risk scores that can help predict personal risk for cardiovascular and renal diseases, as well as African Americans’ treatment responses to common antihypertensive therapies.
COERE awarded $500,000 to provide funds for research supplements to early-career physician-scientists whose research has been impacted by COVID-19.
Tagged under
- release
- school of medicine
- department of medicine
- division of infectious diseases
- division of cardiovascular disease
- center for outcomes and effectiveness research and education
- school of public health
- department of epidemiology
- school of health professions
- department of health services administration
- center for clinical and translational science
Uncontrolled hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a major health concern in underserved communities.
Tagged under