Displaying items by tag: oneal comprehensive cancer center
Join UAB’s Dr. Mona Fouad to hear a discussion on implicit and explicit bias in the field of science and medicine.
The NIH grant creates Multiple Chronic Disease Centers around the nation to target chronic disease in minority populations.
Blood and marrow transplantation strategies have changed significantly over the past four decades; but recipients still experience excess mortality that translates into 8.7 years of life lost, according to researchers in UAB’s Institute for Cancer Outcomes and Survivorship.
This finding upends the long-held paradigm that priming during lung infections takes place only in the draining lymph nodes, and it will be key to developing more efficient vaccinations and therapies for respiratory challenges.
The largest coalition of biological and biomedical research associations in the United States, known as FASEB, advocates for the basic biomedical research community.
The alliance will focus on boosting participation in clinical research within historically underrepresented patient groups.
Gregory Friedman, M.D., has received a special grant to test various therapy combinations with a form of the herpes virus to improve anti-tumor immune response in children battling brain cancer.
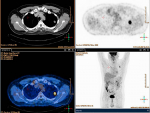
New findings include a significant increase in risk of death among patients who had recently had chemotherapy.