Resection of a 3.5 cm subcutaneous mass from the left hand of a middle-aged man is depicted. What is the most likely cytogenetic abnormality in this tumor? (Brief History)
- t(11;22)
- t(9;22)
- t(7;16)
- t(12;16)
The answer is “D”, t(12;16)
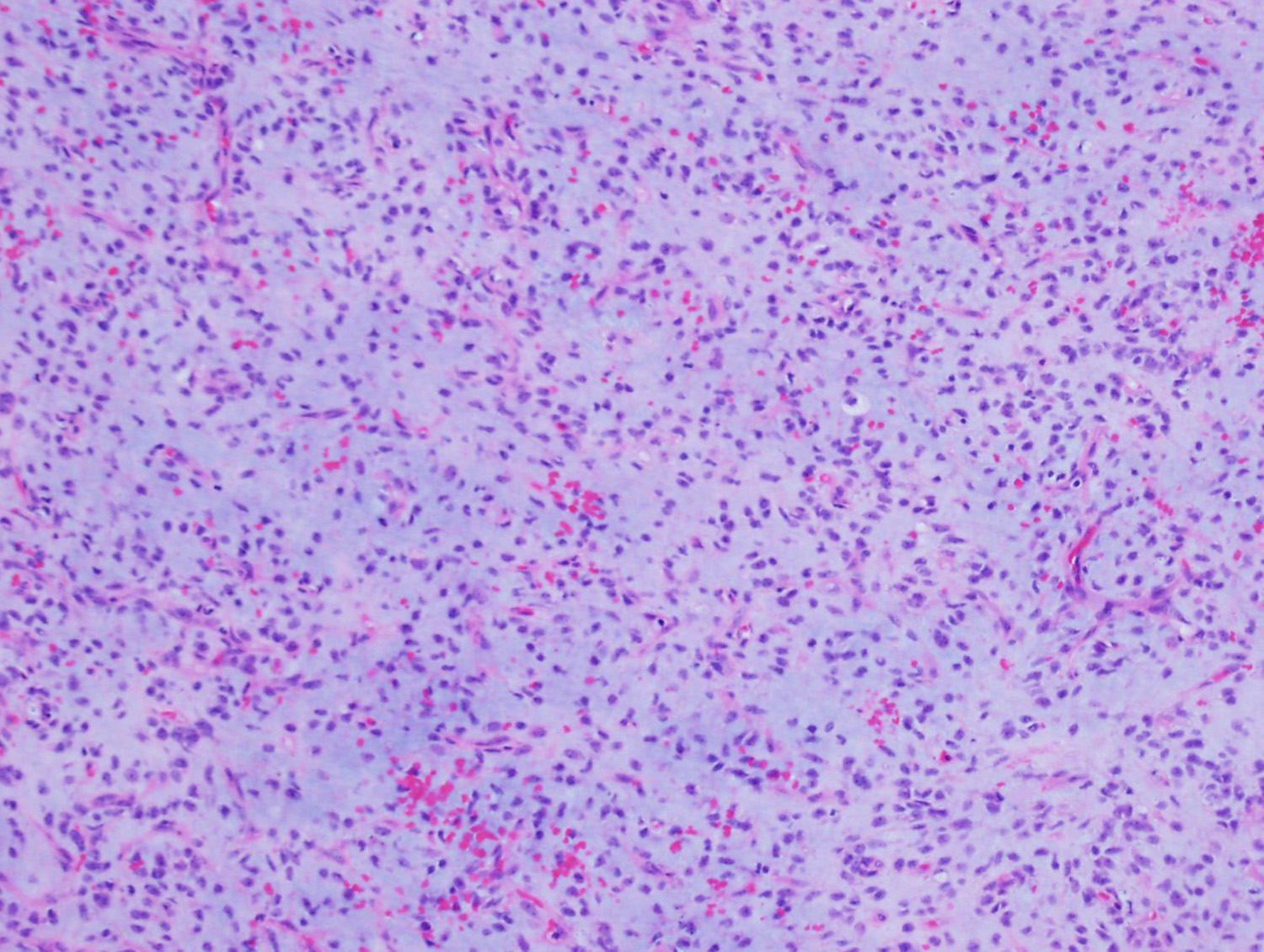
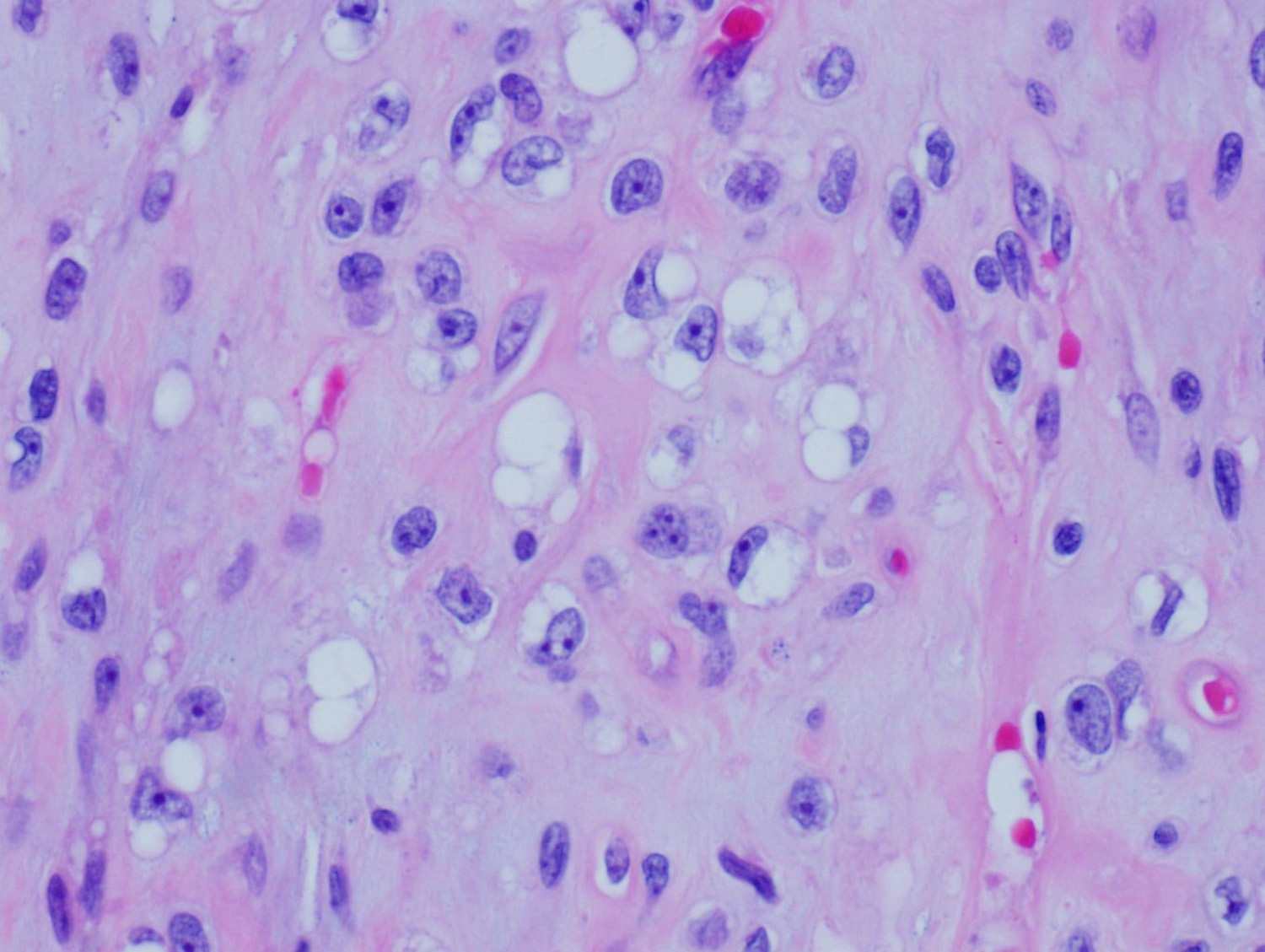
This is an example of myxoid liposarcoma. It usually occurs in young adults, mostly arises in the deep soft tissues of the extremities. On histologic sections, the tumor typically has a nodular growth pattern, with a prominent myxoid stroma and delicate, arborizing, “chicken-wire” vasculature, and often contains “pulmonary edema”-like areas. There is a mixture of small, round, blue cells and small, signet-ring lipoblasts. Myxoid liposarcoma is characterized by t(12;16)(q13;p11) that results in FUS-DDIT3 gene fusion, present in >95% of cases. Rarely, t(12;22)(q13;q12) EWSR1-DDIT3 can be seen.
Choices A, B and C are characteristically seen in Ewing Sarcoma, extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma and low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma, respectively.
References
-
Crozat A, Aman P, Mandahl N, Ron D. Fusion of CHOP to a novel RNA-binding protein in human myxoid liposarcoma. Nature. 1993 Jun 17;363(6430):640-4.
-
Fletcher CDM, Bridge, JA, Hogendoorn PCW, Mertens F. WHO Classification of Tumors of Soft Tissue and Bone. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2013.