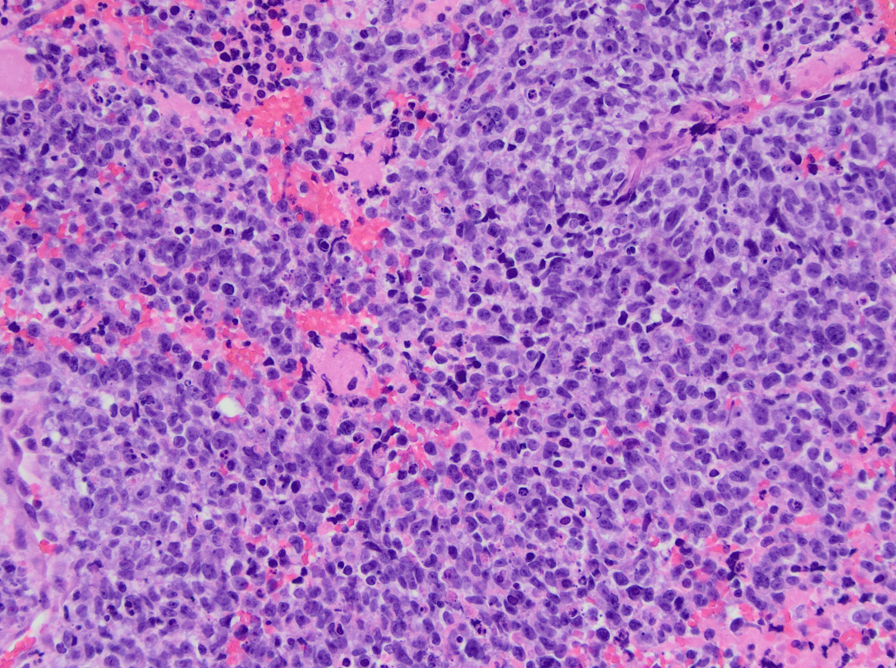
Case History
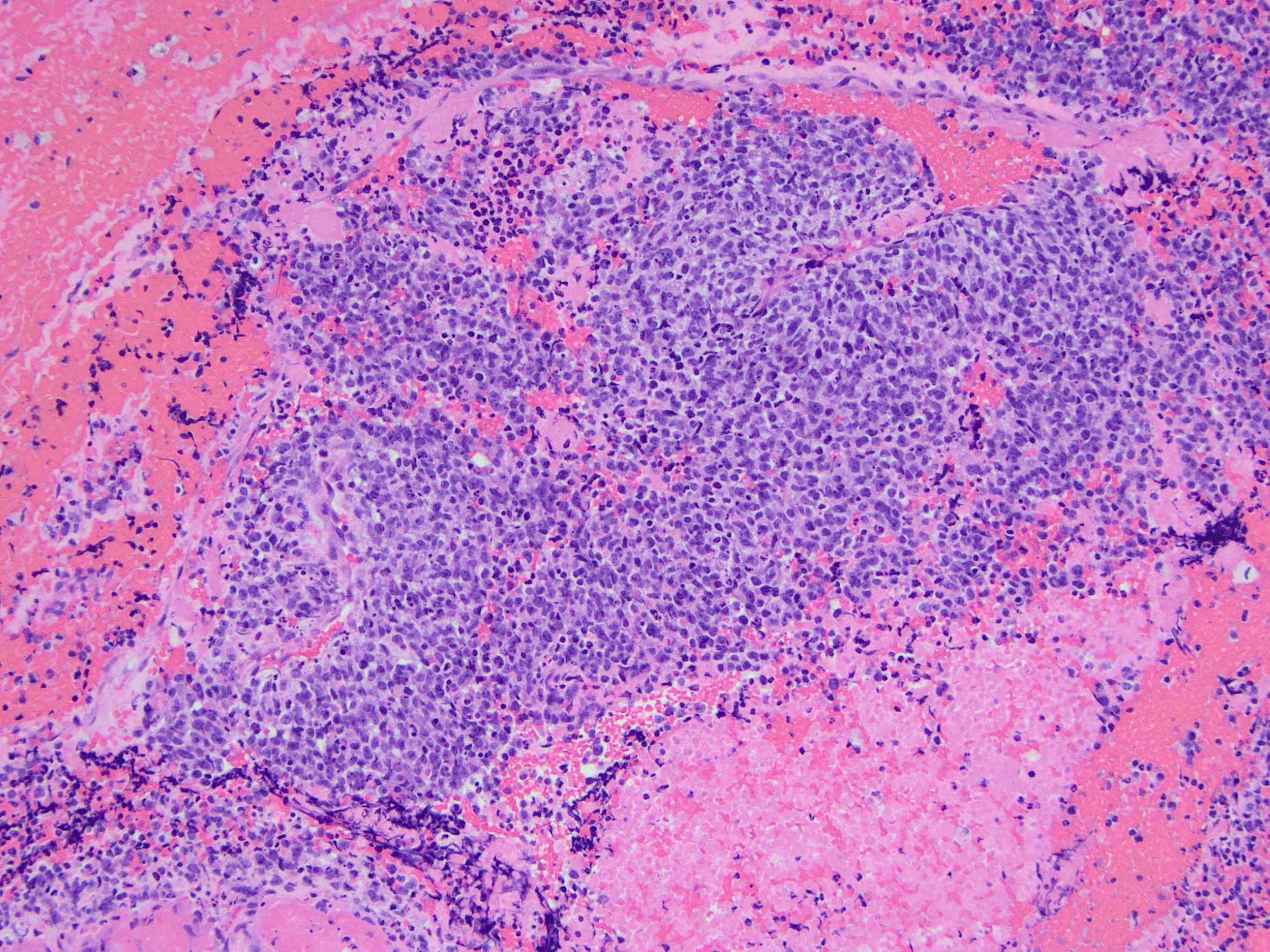
The patient is a 71-year-old female with a lower extremity weakness and a lobulated, solid contrast enhancing intradural intramedullary lesion at C6-T1 levels on MRI. A CT chest, abdomen, and pelvis demonstrated small lesions in the lungs, breast, and liver concerning the possible metastatic disease.
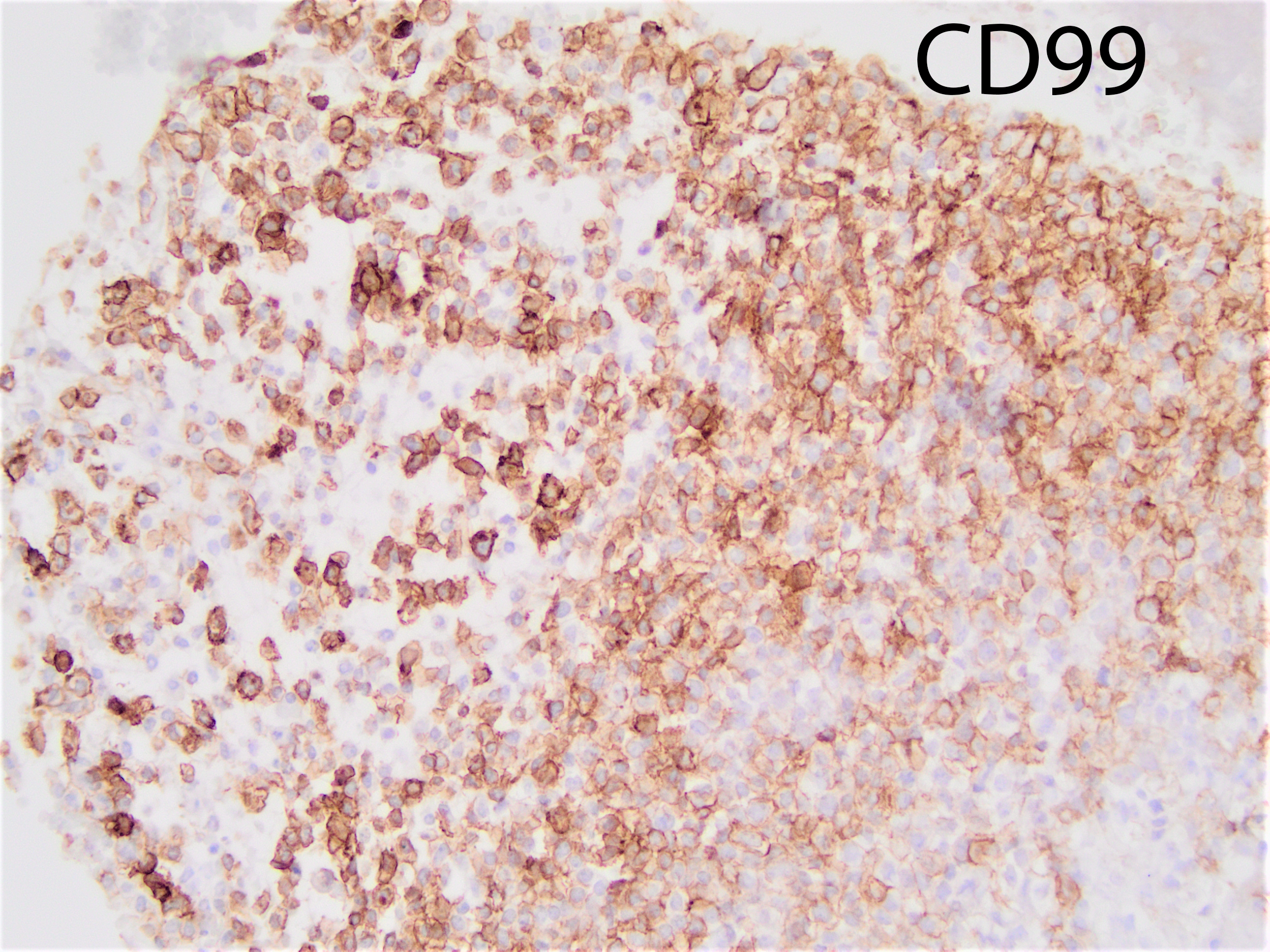
The tumor shows strong cytoplasmic positivity for CD99. The tumor cells are negative for chromogranin, synaptophysin, CK7, CK20, pan-CK, GATA3, HMB45, PAX8, TTF1, p40, and SOX10:
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Anaplastic meningioma
B. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST)
C. Synovial sarcoma
D. CIC rearranged sarcoma
CIC-DUX4 rearranged sarcoma is a small blue round cell tumor resembling Ewing sarcoma. In addition to small blue round cells morphology, CIC rearranged sarcoma may also show focal areas of spindling and epithelioid/rhabdoid phenotype, with frequent myxoid stromal changes. Similar to Ewing sarcoma, it also shows strong cytoplasmic and membranous positivity of CD99. Patient age at presentation ranges from 6 to 70 years (mean age: 32 years). Most of the time it arises in the soft tissue of the trunk and extremities. Overall survival is worse than Ewing sacrcoma.
Anaplastic meningioma usually does not have small round blue cell morphology and C99 positivity is reported as weak and focal in a small subset of anaplastic meningioma cases. 75% of anaplastic meningiomas have been reported to express cytokeratin.
C99 positivity is not characteristic for MPNST. Synovial sarcoma are usually diffuse S100 and patchy cytokeratin positive.
Antonescu CR, Owosho AA, Zhang L, et al. Sarcomas With CIC-rearrangements Are a Distinct Pathologic Entity With Aggressive Outcome: A Clinicopathologic and Molecular Study of 115 Cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2017;41(7):941-949. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000846
Case contributed by: Rati Chkheidze, M.D., Assistant Professor, Neuropathology